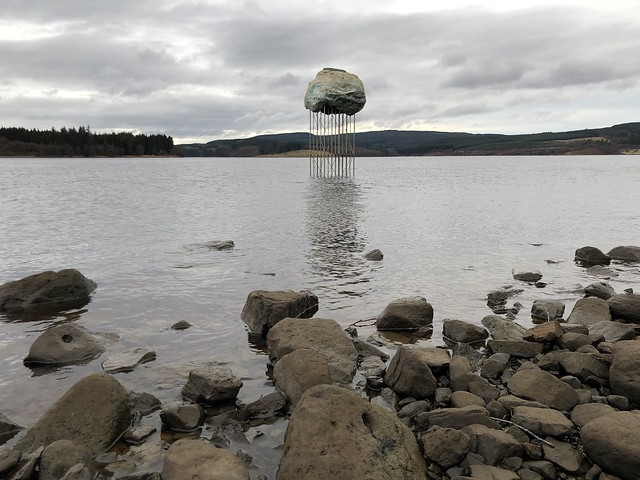Topics > Landmarks, Parks and Buildings > Kielder Water & Forest Park
Kielder Water & Forest Park
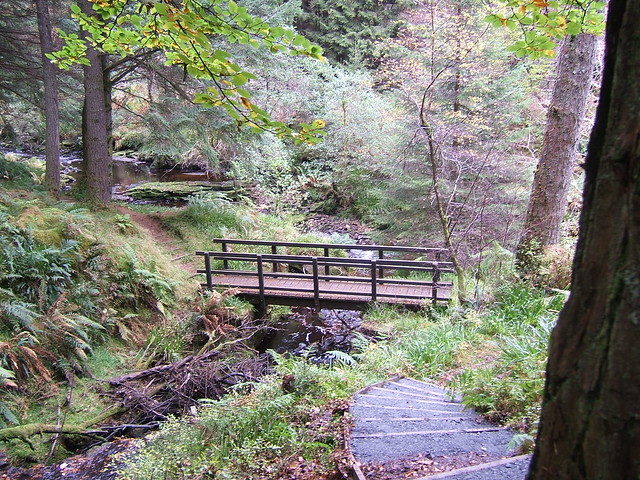
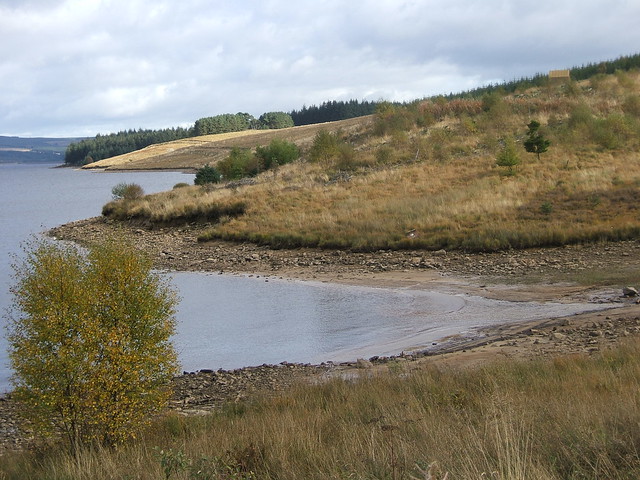
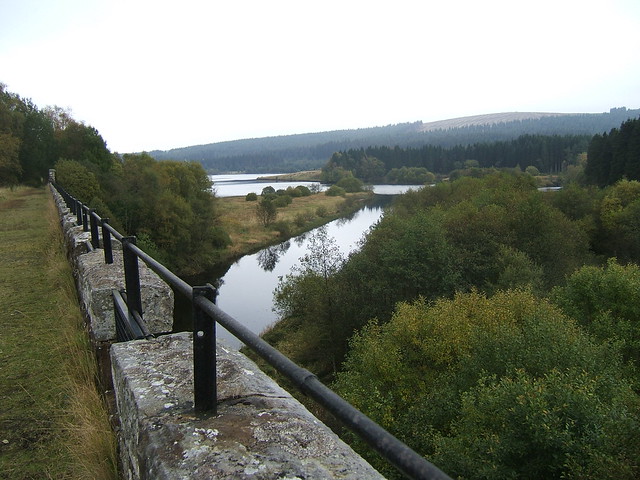
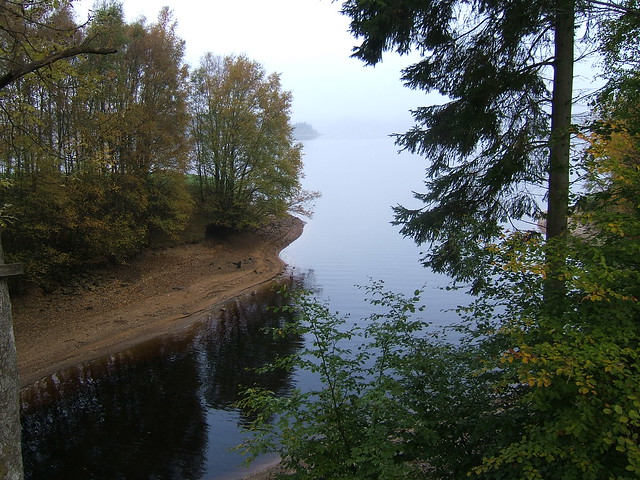
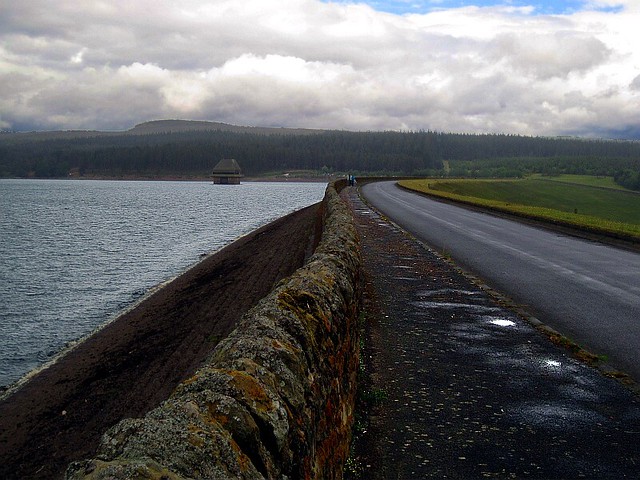
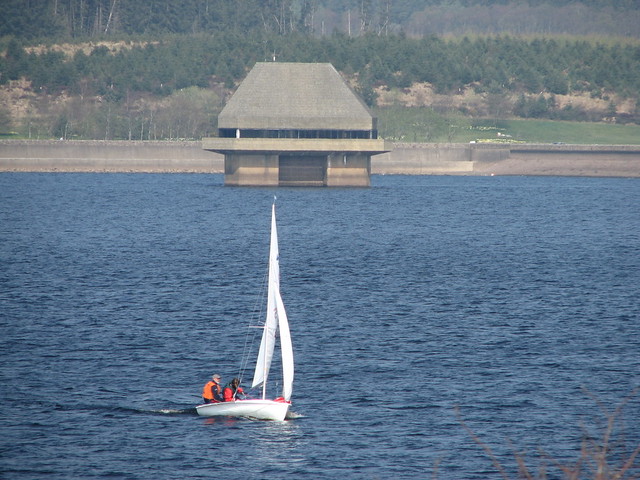
Kielder Water is a large man-made reservoir in Northumberland in North East England. It is the largest artificial lake in the United Kingdom by capacity of water and it is surrounded by Kielder Forest, the biggest man-made woodland in Europe. The scheme was planned in the late 1960s to satisfy an expected rise in demand for water to support a booming UK industrial economy. But the decline of traditional heavy industry, together with more water-efficient industrial processes and better control of water supply leakage, served to undermine the original justification for the reservoir and many came to criticise the government-funded project as a white elephant.
Kielder Water is owned by Northumbrian Water, and holds 200 billion litres (44 billion gallons, or 0.2 cubic km), making it the largest artificial reservoir in the UK by capacity (Rutland Water is the largest by surface area). It has a shoreline, and is 39.7 km (24.6 miles) from the sea.
Construction
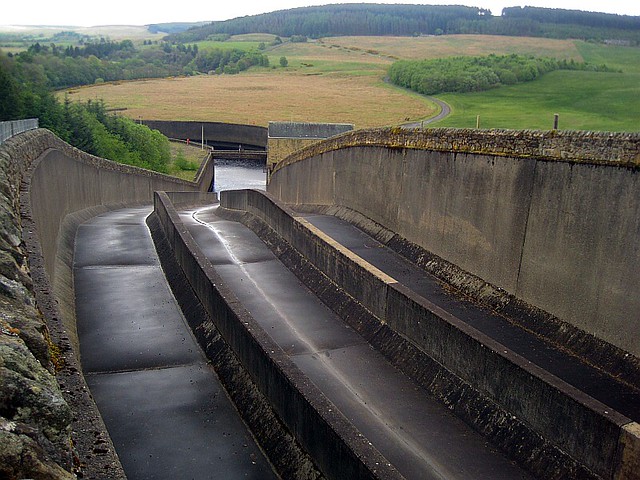
After the scheme was approved by Parliament in 1974, work to build the reservoir and the dam at the hamlet of Yarrow in the Kielder Valley began in 1975. The reservoir and dam was designed for Northumbrian Water by consulting civil engineers Babtie, Shaw and Morton of Glasgow. Sir Frederick Gibberd and Partners were responsible for architectural aspects. Earth moving and infrastructure construction was undertaken in a joint venture with AMEC and Balfour Beatty.
The design meant the loss of numerous farms and a school. The former permanent way of the Border Counties Railway was also taken away through the development of the reservoir.
Work was completed in 1981. Queen Elizabeth II officially opened the project the following year. The valley took a further two years to fill with water completely.
Hydroelectric plant
Kielder Water is also the site of England's largest hydroelectric plant. It was opened by Queen Elizabeth II on 26 May 1982 and is owned by Northumbrian Water. In December 2005, RWE Npower Renewables bought the rights to operate the plant and sell the electricity generated by it, with a contract lasting until 2025. Following the takeover, the turbines were refurbished in 2005–2006, which increased the efficiency of the electricity generation. Controls were also updated, meaning that the plant can be operated from Dolgarrog in Wales.
The plant generates electricity using dual turbines which produce 6 megawatts of electricity. This comes from a combination of a 5.5 MW Kaplan turbine, which generates electricity when water release takes place, and a 500 kW Francis turbine that generates constantly from the compensation flow of water from the reservoir into the North Tyne. This gives the reservoir an average production of 20,000 MWh of electricity per year, a saving of 8,600 tonnes of carbon dioxide per year compared to fossil fuel based methods of generation.
Operations
The reservoir's main use is to provide compensating discharges into the River North Tyne to support abstractions of water further downstream. It also underpins the £167m Kielder Transfer Scheme, where water can be transferred to the Wear and the Tees rivers, to meet shortfalls in those areas. In recent years, Kielder Water has become increasingly important, with underground springs ensuring that it always remains at high levels, regardless of the prevailing climate condition. This means that while the south of England is often forced to implement drought strategies and hosepipe bans, north-east England enjoys plentiful water supplies.
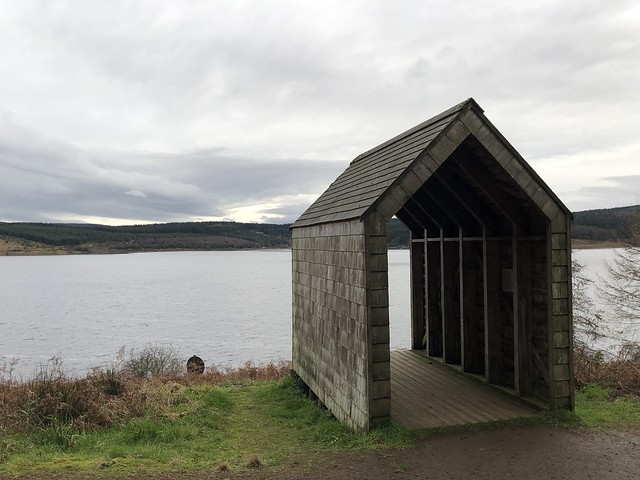
There are two main visitor centres at Kielder Water – Leaplish waterside park and Tower Knowe visitor centre – and other facilities at Kielder, Falstone and Stannersburn villages. It is also one of the region's major tourist venues, attracting more than 250,000 visitors a year who come to enjoy the facilities.
Visit the page: Kielder Water for references and further details. You can contribute to this article on Wikipedia.
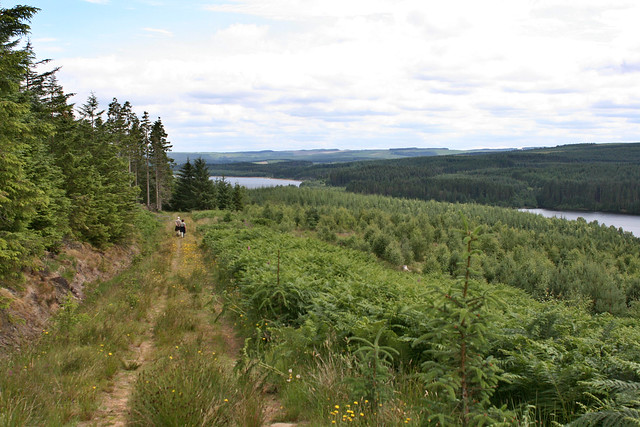
Kielder Forest is a large forestry plantation in Northumberland, England, surrounding Kielder village and the Kielder Water reservoir. It is the largest man-made woodland in England with three-quarters of its covered by forest. The majority of the forest lies within the Border Forest Park, with the southern tip known as Wark Forest lying within Northumberland National Park.
History
The forest is owned and managed by the United Kingdom's Forestry Commission, which initiated the first plantings in the 1920s. During the 1930s, the Ministry of Labour supplied men from among the ranks of the unemployed. Many came from the mining communities and shipyards of North East England. They were housed in one of a number of instructional centres created by the Ministry, most of them on Forestry Commission property; by 1938, the Ministry had 38 Instructional Centres across Britain. The hutted camp in Kielder is now under Kielder Water. Numerous purpose-built villages were also constructed for workers' families, including Stonehaugh.
Prior to the 1920s, the land was predominantly open moorland, managed for grouse shooting and sheep grazing with remnants of native upland woodland existing along stream sides and in isolated craggy areas. The Forestry Commission, funded from the public purse, purchased land across the country with the brief of establishing a strategic reserve of timber for the nation. This single objective held sway until the 1960s. Since that time, management principles have changed in order to reflect rising awareness of environmental needs and to provide recreational facilities whilst seeking to maintain a sustainable supply of timber. Kielder today remains state-owned and its development from a single-objective plantation to a multi-purpose forest mirrors the development of plantation forestry across the United Kingdom.
Many archaeological remains can be found within the forest and are an important cultural link to the often turbulent history of the area.
Geography
The name 'Kielder Forest' is often also applied to the area of hills and remote moorland that surround the forestry plantations. The group of hills merges into the Cheviots to the north-east but is generally well-defined on other sides. It reaches a maximum height of at Peel Fell and also contains the Marilyns of Sighty Crag and Larriston Fells. These hills, despite not being very high, are particularly remote owing to the scarcity of settlement in the region. Indeed, Sighty Crag is the furthest hill in England from a road, at four miles' distance.
Environment
Trees
Kielder is dominated by conifers. Sitka spruce (Picea sitchensis) covers 75% of the planted area; this species thrives in the damp conditions afforded by northern Britain. Other species include Norway spruce (Picea abies) and lodgepole pine (Pinus contorta), which cover 9% of the area each. The remainder is made up of Scots pine (Pinus sylvestris), larch (Larix spp.), Douglas-fir (Pseudotsuga menziesii), and broadleaves including birch (Betula spp.), rowan (Sorbus aucuparia), cherry (Prunus spp.), oak (Quercus spp.), beech (Fagus sylvatica), and willow (Salix spp.).
Timber
475,000 cubic metres of timber is harvested annually to supply local sawmilling, chipboard, pulp and wood fuel customers. Most of this volume comes from clearfelling areas; an increasing percentage however is sourced from stands harvested under continuous cover silviculture systems. Clear felled areas are replanted with a mix of coniferous and broadleaf tree species, opportunities are also taken to increase the proportion of open space and to improved the riparian habitat. As with all Forestry Commission woodlands timber is independently certified under the Forest Stewardship Council scheme.
Wildlife
The forest contains a number of sites of special scientific interest, primarily associated with the upland moorland environment. A programme of restoration of Border mires is ongoing.
The forest is also home to around 50% of England's red squirrel population, and is their biggest remaining stronghold in the country. The best place to catch a glimpse of one is at the squirrel hide at Kielder waterside.. It also provides excellent habitat for many species of birds of prey. In 2009 a pair of osprey (Pandion haliaetus) nested successfully in the forest. This pair have continued to nest there each year since, and a second pair nested in 2011. In 2014 eight young were fledged and by 2016 there were four nesting osprey pairs fledging eleven young. A large population of roe deer is actively managed.
Due to the low human population and scarcity of roads and railways, Kielder Forest was proposed in July 2016 as one of the preferred reintroduction sites for the Eurasian lynx, which has been extinct in Britain for 1,300 years. Interest in reintroducing the species was further bolstered in 2016 in relation to a successful breeding program for the Iberian lynx in Spain.
Recreation
Kielder Castle
Kielder Castle Visitor Centre is an 18th-century hunting lodge built by the Duke of Northumberland, which has been converted into a visitor and information centre. It is located on the edge of Kielder Village at the head of the River North Tyne valley. The Castle serves as a hub for the growing number of recreational facilities on offer, walking and cycling trails, picnic areas and a forest drive. A great football match is reported to have taken place between the men of Tynedale and Redesdale at Kielder Castle in 1790.
Other attractions
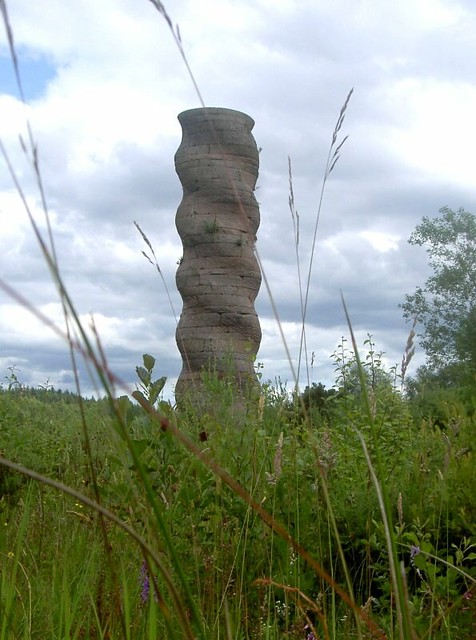
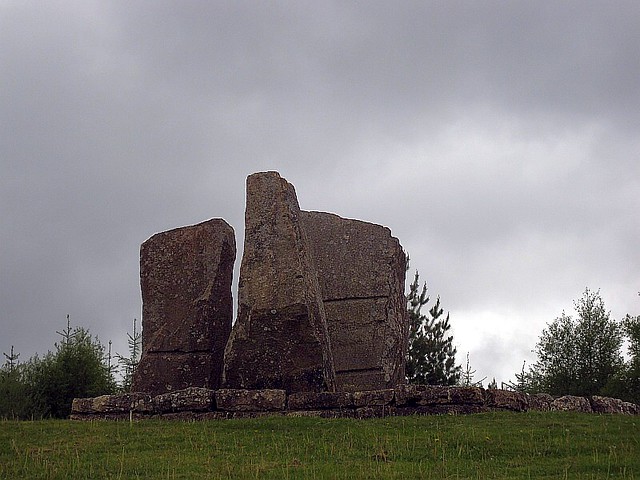
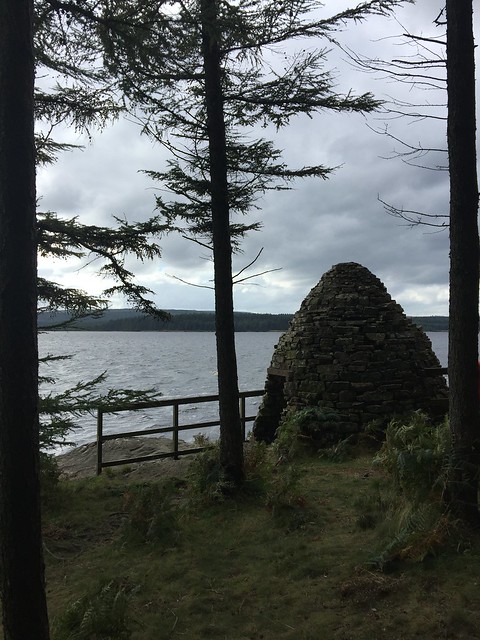
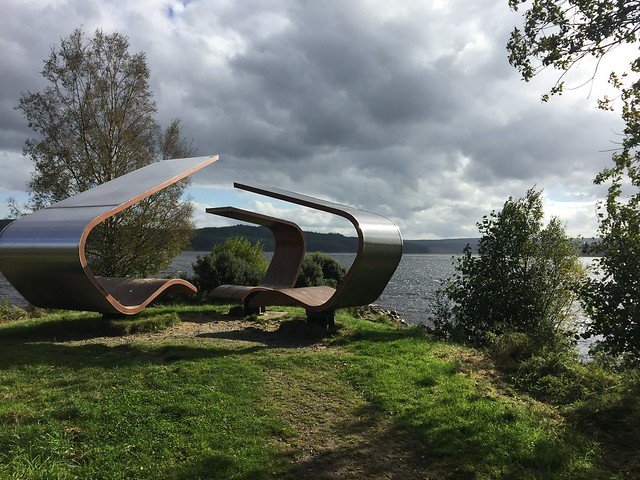
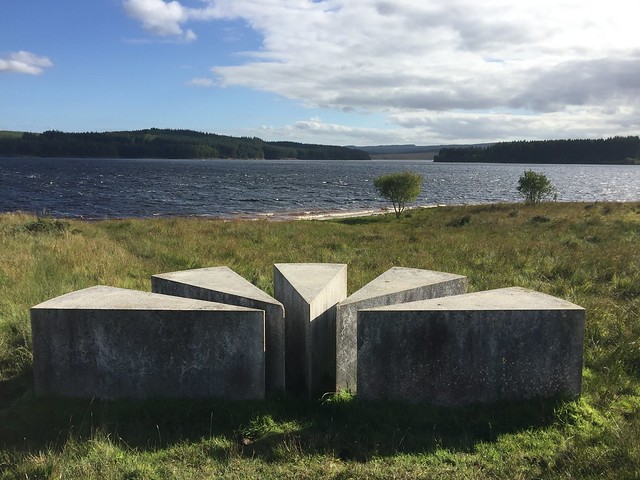
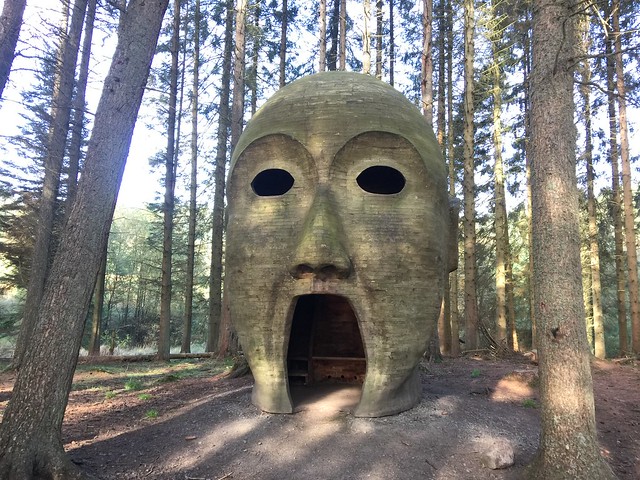
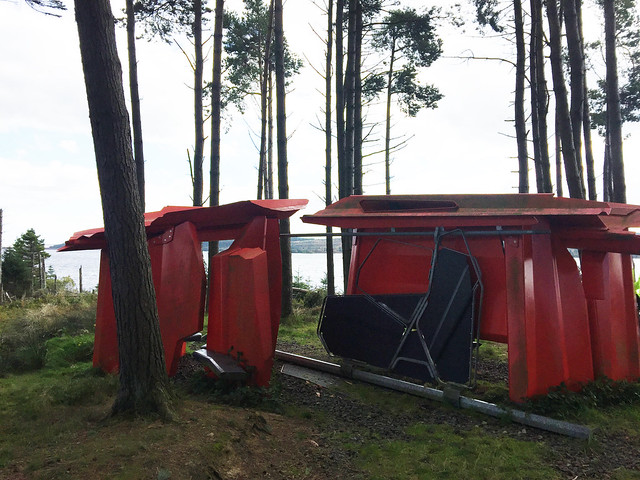
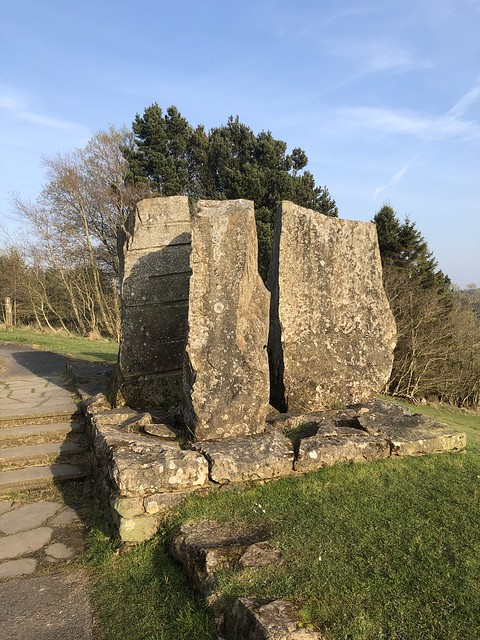
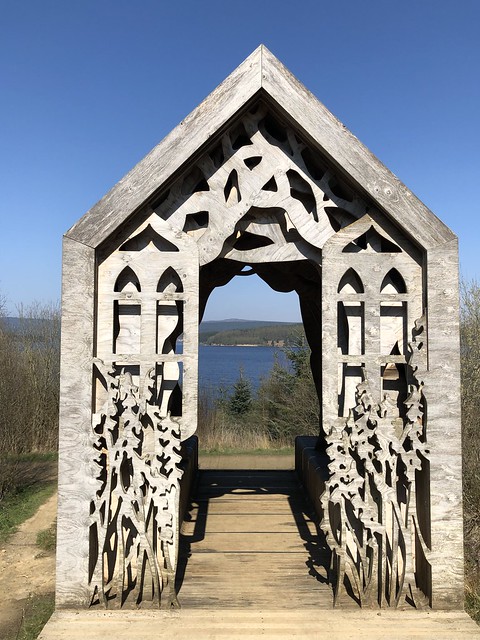
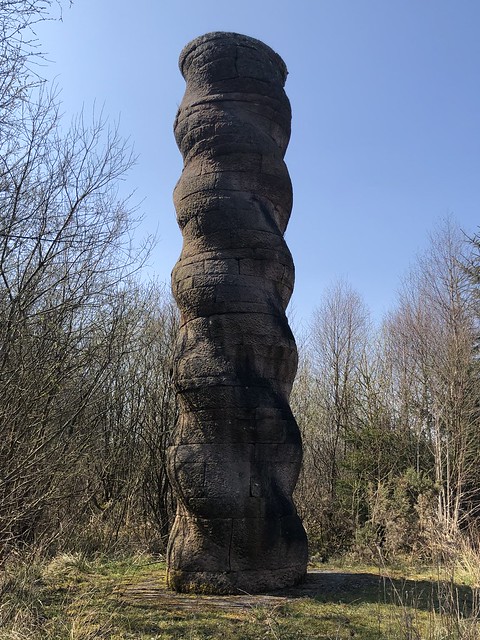
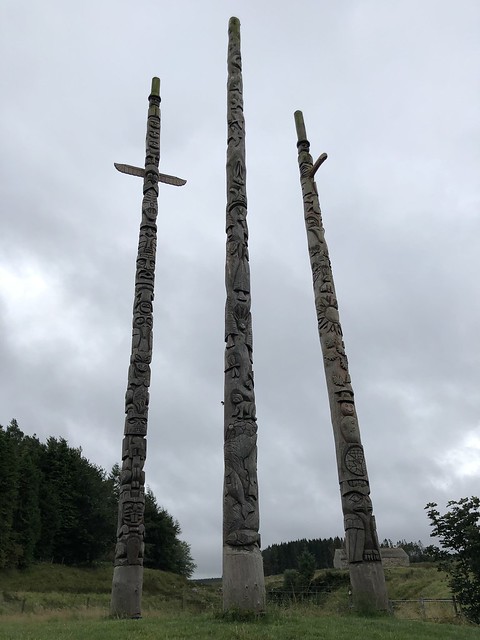
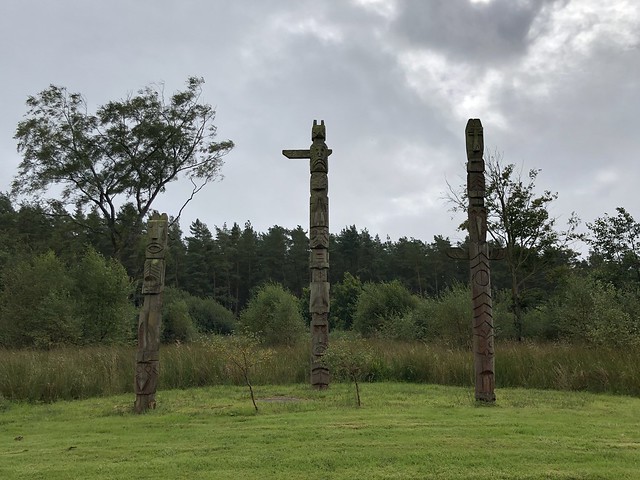
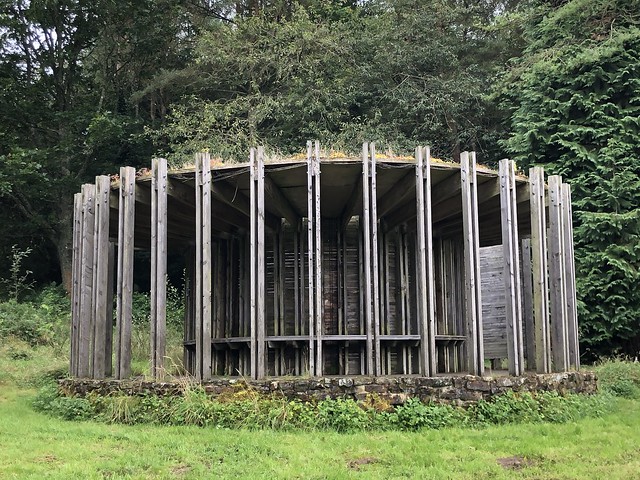
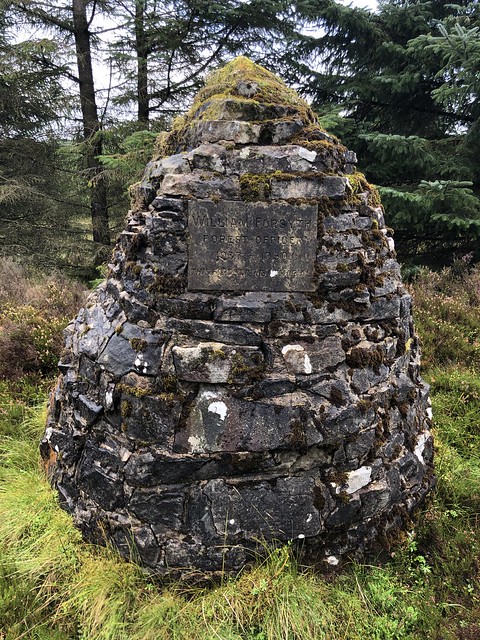
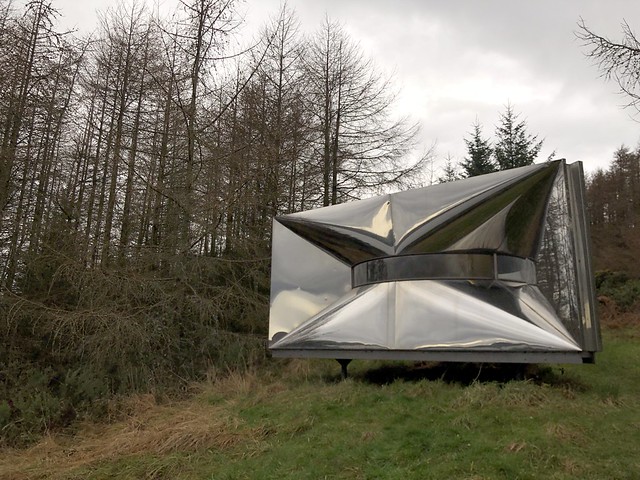
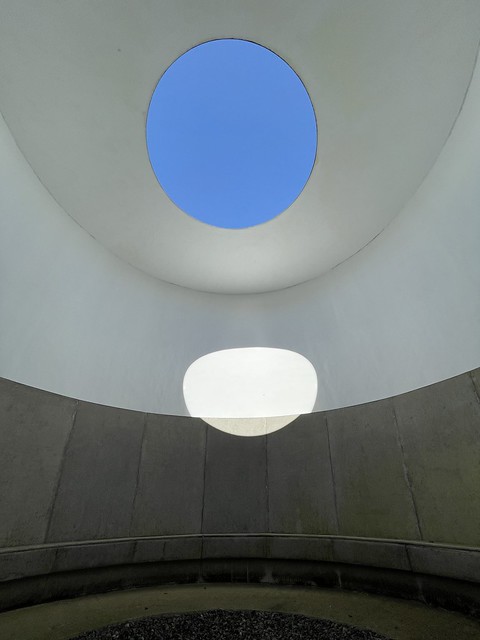
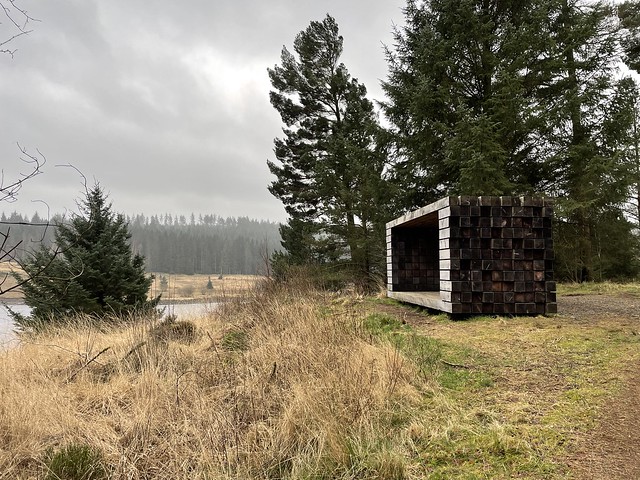
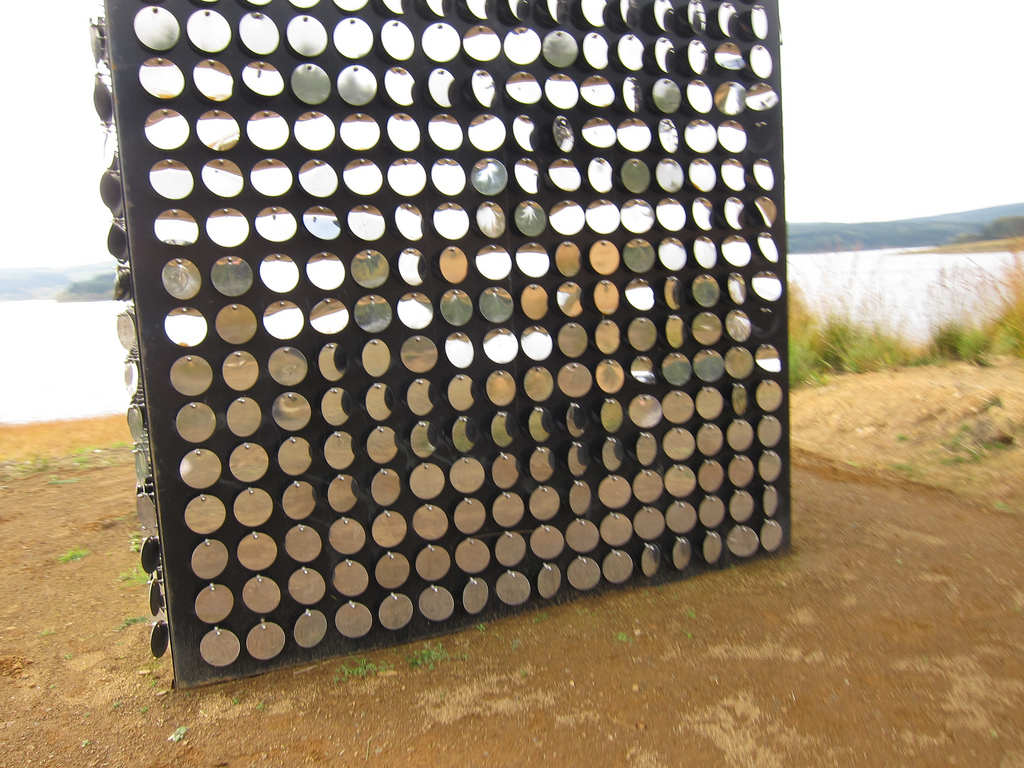
The forest contains a number of art and architectural installations including a Skyspace designed by James Turrell and Wave Chamber, a camera obscura in a stone cairn by Chris Drury.
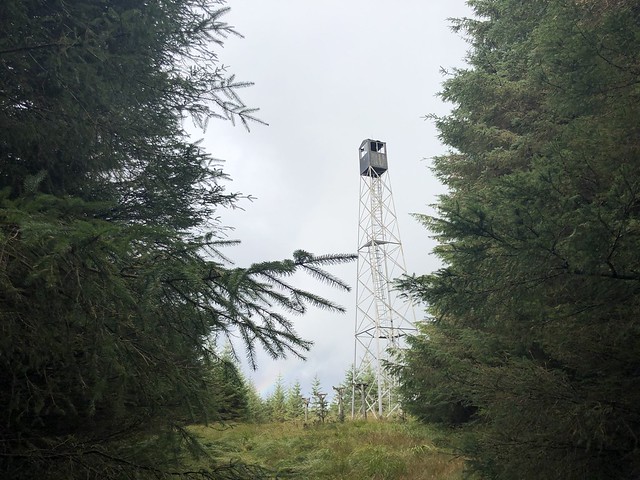
The forest also contains Kielder Observatory which is an astronomical observatory.
In 2010, former British distance runner Steve Cram inaugurated the Kielder Marathon which is a circuit around the lake taking in the surrounding gentle contours.
In the same decade the local authority began a reduction of late night street lights to enhance the dark skies of the park and sponsored observation facilities and advertising to attract visitors to the darkest skies in the mainland of Britain.
Visit the page: Kielder Forest for references and further details. You can contribute to this article on Wikipedia.

from http://www.visitkielder.com/
Kielder Water & Forest Park
- Official Website of Kielder Water & Forest Park. The Development Trust is a registered charity with a membership of Northumbrian Water, Forestry Commission, Calvert Trust Kielder, and Northumberland County Council.
Added by
Simon Cotterill
from Flickr (flickr)
Kielder -- Kielder Marathon - 2010 -- Sun 17 Oct 2010 11-14-36 AM BST.jpg
Pinned by Simon Cotterill

from Flickr (flickr)
Kielder -- Kielder Marathon - 2010 -- Sun 17 Oct 2010 08-53-44 AM BST.jpg
Pinned by Simon Cotterill

Co-Curate Page
Kielder
- Overview About Kielder Map Street View Kielder Village is a small, remote village in western Northumberland, England. Located at the head of Kielder Water and in the north west …

Co-Curate Page
Yarrow
- Overview Map Street View Yarrow is a hamlet in Northumberland on the south banks of the River North Tyne. Yarrow is immediately east of Kielder Water and west of Falsone …

from http://www.visitkielder.com/
Kielder Water & Forest Park
- Official Website of Kielder Water & Forest Park. The Development Trust is a registered charity with a membership of Northumbrian Water, Forestry Commission, Calvert Trust Kielder, and Northumberland County Council.
Added by
Simon Cotterill

from Flickr (flickr)
Kielder -- Kielder Marathon - 2010 -- Sun 17 Oct 2010 11-14-36 AM BST.jpg
Pinned by Simon Cotterill

from Flickr (flickr)
Kielder -- Kielder Marathon - 2010 -- Sun 17 Oct 2010 08-53-44 AM BST.jpg
Pinned by Simon Cotterill

Co-Curate Page
Kielder
- Overview About Kielder Map Street View Kielder Village is a small, remote village in western Northumberland, England. Located at the head of Kielder Water and in the north west …