Topics > County Durham > Streatlam > Streatlam Castle (demolished 1959)
Streatlam Castle (demolished 1959)
Extract from: Francis Grose & Thomas Astle, The Antiquarian Repertory....(1809):
Streatlam Castle
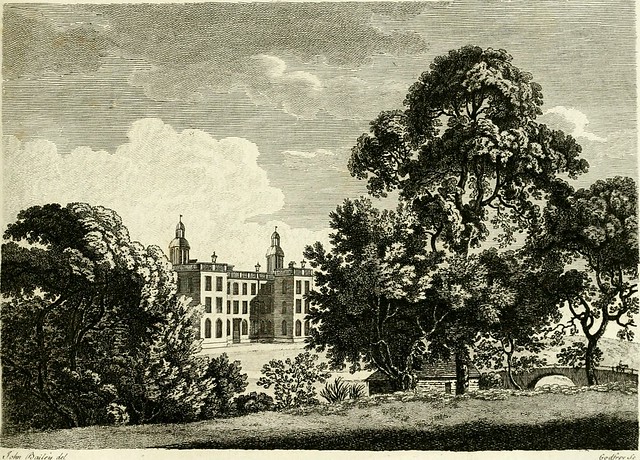

IS situate in the western part of the county of Durham, within two miles of Barnard Castle; is a modern structure, built of excellent free-stones, and after an elegant plan.
Nothing but a veneration for the ancient seat of the family, could induce the proprietor to erect such a mansion, in so ineligible a situation. It stands in a deep vale, a small brook runs close to its front, high and irregular hills arise on every side, in some parts covered with a forest of oaks ; and the whole aspect is solemn. The opposite grounds are occupied as a park for deer, and afford a narrow prospect. There is something romantic in these secluded scenes, which please the contemplative mind; but they are better adapted to the vicinity of a cottage than a palace. The purling brook, the broken cliff, from whose shaken sides old oaks impend, and cast a long extended shadow over the narrow dell ; the ivy-twisted elm, the mossy cove and primrose bank, are pretty objects in pastoral life, but correspond not with the gaiety of the great. Such are the beauties of Streatlam.
Streatlam was part of the possessions of Bernard Baliol, grandfather of John, King of Scotland ; he was Baron of Bywell in Northumberland, and founder of Barnard Castle. He gave this castle and lordship, with divers adjoining lands, in dowry with his niece Agnes, who married Sir John Trayne. Sir John's son and immediate successor having one child, Alice, his heiress, she married Sir Adam Bowes, Knight, Justice in Oyer of the liberties of Durham, and Steward of Richmondshire, about the year 1310, when Streatlam became the possession of the family of Bowes, who are owners of it at this time. In what state the castle was at that period is not known. After several regular descents, Streatlam became the possession of Sir William Bowes, who received the order of knighthood at the battle of Vernoyle in France, in the year 1424. He was Chamberlain to John, Duke of Bedford, Regent in France during the minority of King Henry VI. and was by him made Governor of the Castle of Gallyard in Normandy; he continuing in France about twenty years. During this time, he sent over a model for rebuilding his castle of Streatlam, in which he afterwards lived to a great old age. The castle, built after such model, remained to the beginning of the 18th century, when the present structure was erected on the same ground. Some of the old steps in the ascent are yet remaining.
Streatlam Castle was a Baroque stately home located near the town of Barnard Castle in County Durham, England, that was demolished in 1959. Owned by the Bowes-Lyon family, Earls of Strathmore and Kinghorne, the house was one of the family's three principal seats, alongside Glamis Castle in Forfarshire, Scotland and Gibside, near Gateshead. Streatlam incorporated some of land, along with an estate consisting of some twenty farms. The last occupant was Lord Glamis, who later became the 15th Earl, although the estate was owned by his father, the 14th Earl, at the time.
History
The House had come to the Bowes family by the fifteenth century. For much of the nineteenth century, it was owned by John Bowes, the eldest son of the 10th Earl of Strathmore who was illegitimate under English law as his parents married after he was born (and under Scottish law as they had no Scottish domicile), but was able to inherit a life interest in the family's English wealth and properties. During his tenancy, Streatlam was described as consisting of twenty-four bedrooms, two oak drawing-rooms, the yellow drawing room, the great dining room, the billiard-room, the study and the gentlemen's room.
Following his death without issue, the estate was reunited with the Earldom in 1885. Unlike the fate of other properties which belonged to the Bowes-Lyon family, such as Gibside (which lay within a major coalfield near Gateshead and so was considered spoilt by pollution from the surrounding coal mines),
Streatlam sat amid the beautiful countryside of the Durham Dales.
Decline and demolition
The last occupier was Lord Glamis, heir to the Earldom, who had been living there since at least 1915. The Earl of Strathmore was determined to sell off the house and the land, however, and the bulk of the estate was sold to private tenants, with the remainder fetching £100,000 at auction.
Lord Glamis moved to a substantial farm near East Grinstead, where he resided until he succeeded his father as Earl of Strathmore in 1944.
Some see it as little surprise that the Earl of Strathmore chose Glamis Castle over Streatlam, the house being considered architecturally "awkward and unsatisfactory" (as was claimed in Country Life Magazine in 1915). Also, as the aristocratic titles of the last owner and occupant would suggest, Streatlam was less important in historical terms. Another possible reason is that, for much of the nineteenth century, the Scottish and English estates had been split, with Streatlam and Gibside owned by John Bowes and his wife, which meant that that Scottish branch of the Bowes-Lyon family, namely the Earls of Strathmore, had not been in ownership or residence at Streatlam for from 1820 to 1885, thereby becoming more focused on their Scottish estates. The English estates only reverted to the Earl and his descendants when John Bowes died without issue, leaving his fortune to his first cousin once removed, the 13th Earl, in 1885.
Although there was no pressing financial need to sell at the time, with the family still earning a substantial income from the estate's coal mining holdings, in the end the house was simply considered superfluous. The Earl also owned Wemmergill in County Durham, St Paul's Walden Bury in Hertfordshire and the Gibside estate in Gateshead. It was also a time when many aristocratic families were seeking to cut back on ostentatious displays of wealth following the destruction of the nobility in the Russian Revolution, plus there was a shortage of domestic servants following the First World War.
Lady Strathmore, though ill at the time, hurried down to Streatlam to rescue as many items as possible, many of which were taken to Glamis Castle. The armorial ceiling, installed at Streatlam by John Bowes, were moved to the Bowes Museum, which he had established.
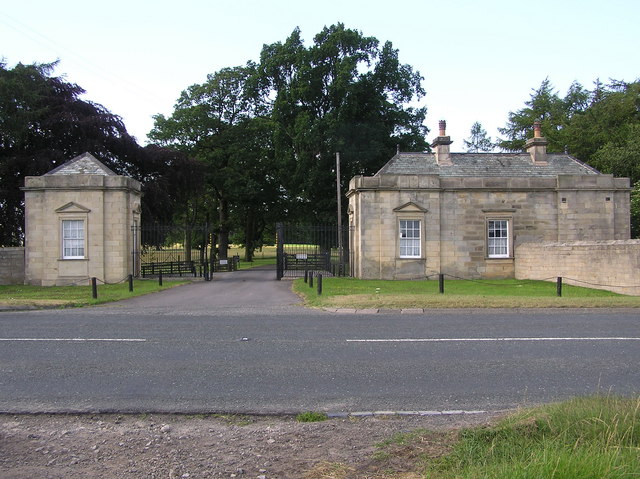
After World War II, many country houses were being demolished. Finally in 1959 the shell was blown up as a training exercise by the Territorial Army. Today only Streatlam Park and its entrance lodges (shown above) remain.
An exhibition on the history of Streatlam Castle opened at the Bowes Museum in November 2017, and then moved to Glamis Castle in March 2018. It included paintings previously displayed at the property, and scale models of the castle and the estate.
Visit the page: Streatlam Castle for references and further details. You can contribute to this article on Wikipedia.
from https://www.thenorthernecho.c…
Streatlam Castle - blown up by the Army in 1959 was once home to the 10th richest man in England
- Northern Echo: 29th November 2017. "ONCE Streatlam Castle was the home of the tenth richest man in England. He filled it with some of his most prized and personal possessions, …
Added by
Simon Cotterill

from https://www.thenorthernecho.c…
Streatlam Castle - blown up by the Army in 1959 was once home to the 10th richest man in England
- Northern Echo: 29th November 2017. "ONCE Streatlam Castle was the home of the tenth richest man in England. He filled it with some of his most prized and personal possessions, …
Added by
Simon Cotterill