Topics > Carlisle > Carlisle Railway Station
Carlisle Railway Station
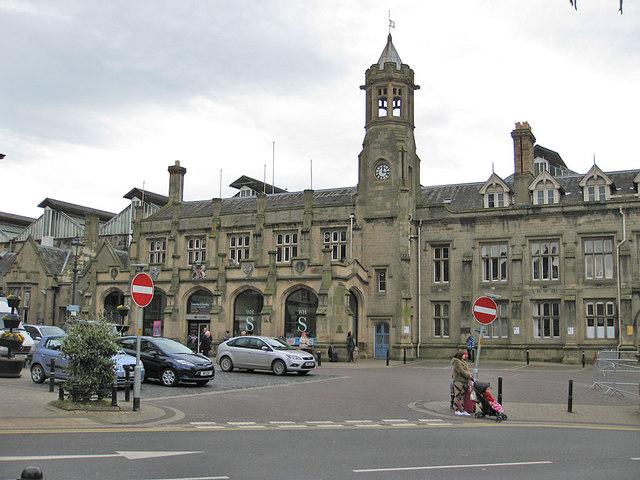
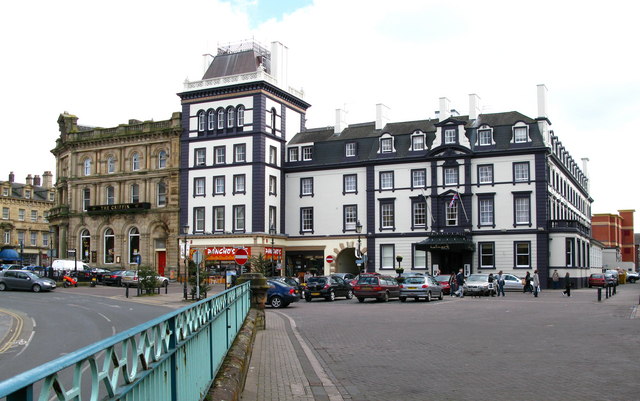
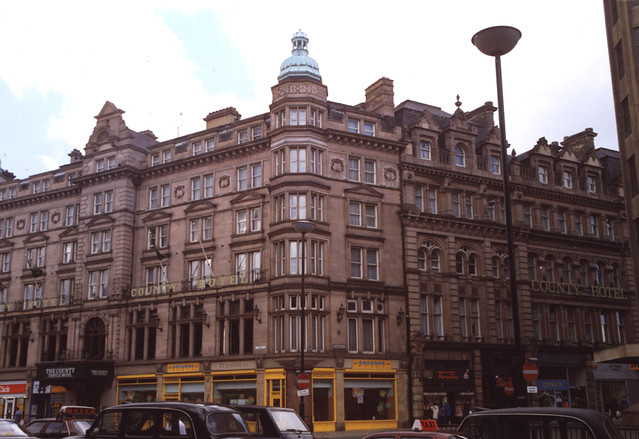
Carlisle Citadel Station was built by the Lancaster and Carlisle Railway and Caledonian Railway in 1847; the crests of both companies can be seen on the outside of the main station building. The station is close to Carlisle Citadel, after which it was named. The first trains from the station ran on the 1st September 1847. Today, Carlisle railway station is owned by Network Rail and serves the West Coast Mail line and is the northern terminus of the Settle and Carlisle Railway. The station is Grade II* listed on the National Heritage List for England.
Carlisle railway station, or Carlisle Citadel, is a Grade II* listed railway station serving the city of Carlisle, Cumbria, England. It is on the West Coast Main Line, 102 miles (164 km) south east of Glasgow Central, and 299 miles (481 km) north north west of London Euston. It is the northern terminus of the Settle and Carlisle Line, a continuation of the Midland Main Line from Leeds, and Sheffield. It is so named because it is adjacent to Carlisle Citadel, a former medieval fortress. The station is owned by Network Rail.
In September 1847, the first services departed the station, even though construction was not completed until the following year. It was built in a neo-Tudor style to the designs of English architect William Tite. Carlisle Station was one of a number of stations in the city, the others were Crown Street and London Road, but it was the dominant station by 1851. The other stations had their passenger services redirected to it and were closed. Between 1875 and 1876, the station was expanded to accommodate the lines of the Midland Railway which was the seventh railway company to use it.
The Beeching cuts of the 1960s affected Carlisle, particularly the closure of the former North British Railway lines to Silloth, on 7 September 1964, and the Waverley Line to Edinburgh via Galashiels on 6 January 1969. The closure programme claimed neighbouring lines, including the Castle Douglas and Dumfries Railway and Portpatrick Railway (the "Port Road") in 1965, resulting in a significant mileage increase via the Glasgow South Western Line & to reach Stranraer Harbour, and ferries to Northern Ireland. The station layout has undergone few changes other than the singling of the ex-NER Tyne Valley route to London Road Junction in the 1972–73 re-signalling scheme, which was associated with the electrification of the West Coast Main Line (WCML). Renovations to the platforms and glass roof were performed between 2015 and 2018.
History
Construction and early operations
Close to the English border with Scotland, Carlisle became an important railway interchange in the first half of the 19th century. In 1836, Carlisle's first station opened at London Road for the Newcastle and Carlisle Railway; seven years later, Crown Street opened for the Maryport & Carlisle Railway. In the mid-1840s, work commenced on Carlisle Citadel on the south side of Court Square. Citadel station was built for the Lancaster & Carlisle Railway and the Caledonian Railways.
Carlisle station was designed by the architect William Tite. His design incorporated Tudor and Gothic styles. Built at a cost of £53,000, the station was constructed between 1846 and 1848. On 10 September 1847, it was officially opened to rail traffic, even though construction was incomplete and only one long through platform with a bay at each end had been finished.
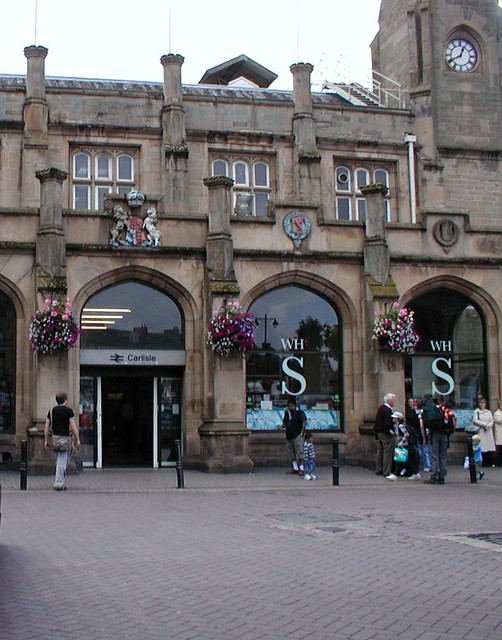
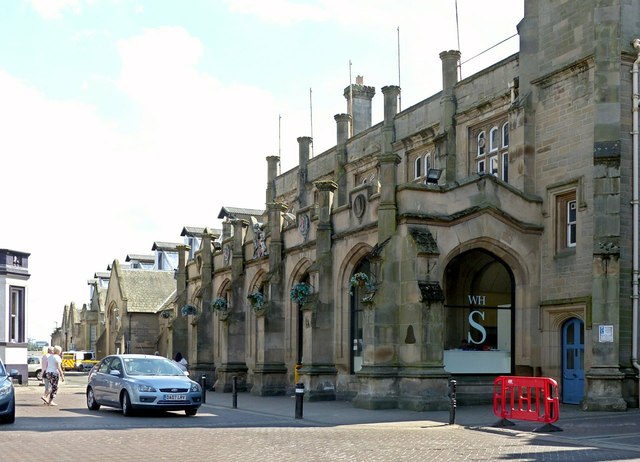
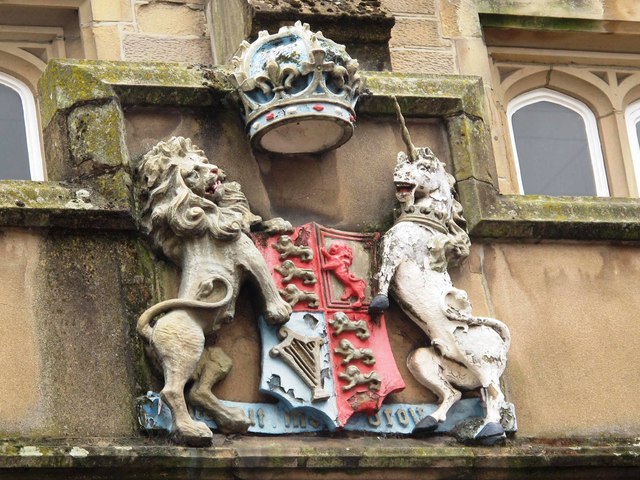
The main station buildings have a multi-bay sandstone facade of two storeys, capped by rows of slate roofs at differing levels. The entrance portico is supported by five pointed arches with buttresses between. Roundels are placed over three arches; the central roundel bears the royal arms of Queen Victoria, flanked by those of the Lancaster & Carlisle and the Caledonian Railways but the outer plaques, intended for the Maryport & Carlisle and the Newcastle and Carlisle who did not contribute towards the cost of the station's construction, are blank.
As a consequence of the station accommodating the complex timetables operated by two, and eventually seven operating companies, a joint management committee was established. On 10 May 1857, the Carlisle Citadel Station Agreement was drawn up and established under the Carlisle Citadel Station Act of 22 July 1861. The committee had eight directors, four each from the boards of the Caledonian and the London and North Western Railway (L&NWR) which had absorbed the Lancaster & Carlisle in 1859.
To improve freight services the Carlisle Goods Traffic Committee was formed after the Carlisle Citadel Station Act of 1873. The London & North Western, Midland, Caledonian and Glasgow & South Western each had two directors on the committee. To minimise the danger to passengers, a goods avoidance line was constructed to divert freight trains around the station.
Expansion and later service
The Carlisle Citadel Station Act authorised changes, not restricted to freight, including an instruction "enlarging and improving facilities". Expansion work took place between 1873 and 1876 followed by a second phase between 1878 and 1881. While construction was taking place, the opening of the Midland Railway's Settle–Carlisle line generated more freight trains from August 1875, and passenger services, started in April 1876.
On 20 July 1881 improvements were officially completed. Carlisle station was used by seven railway companies, the London and North Western, London North Eastern, Midland, Caledonian, North British, Glasgow & South Western and Maryport & Carlisle. Each companies operated its own passenger amenities with separate booking and parcels offices.
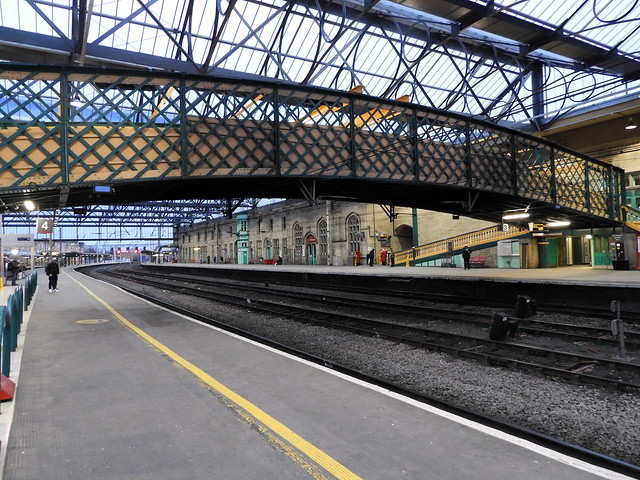
Additional tracks, buildings and platforms were constructed including an island platform with two-storey buildings which increased the 400 metre-long through platforms to three. Five terminal bay platforms were constructed and an overarching footbridge which connected the through platforms inside the train shed. Below the platforms, the undercroft contains a network of passageways, offices, service rooms and staff accommodation; parts of the underground areas are reputed to be haunted.
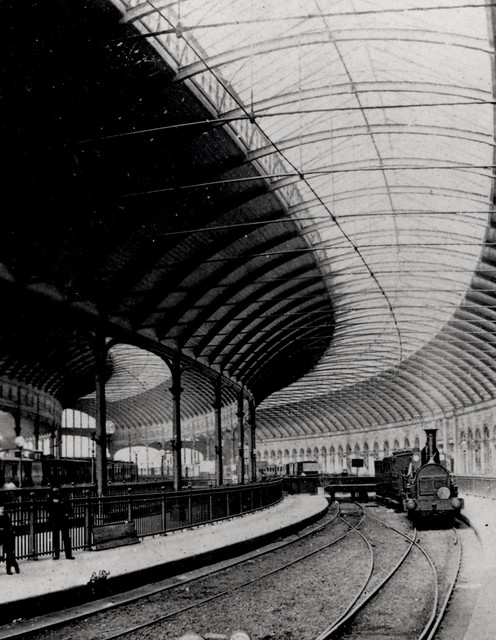
During the construction programme an iron and glass large roof was installed behind the station buildings. As built, it spanned 85 metres across the platforms and tracks to cover an area in excess of 2.6 hectares. It consisted of 26 deep lattice girders, with a transverse span and 12.2 metre centres; each girder had 10 panels, stiffened end posts and a flat bottom tie. The girders supported a series of slender balanced cantilever half-truss hooped beams at approximately 3.7m centres, spanning the tracks. The ornate timber end screens had Gothic-style glazing bars. The roof was glazed using shingled panels, possibly making use of Rendel's patented Indestructible System, and was designed by Edinburgh-based engineering firm Blyth & Cunningham.
Twentieth century
During 1922, five of the seven companies that operated at the station were absorbed into the London Midland & Scottish Railway (LMS) after the Railways Act 1921. During the Second World War, black paint was applied to the roof glazing as a precautionary measure against enemy air raids.
Preventative maintenance gradually led to large areas of the glass roof becoming unsafe and forcing occasional platform closures after falling glass. In 1957 it was decided to reduce the area of the roof and concentrate maintenance activities on the remaining area. Between 1957 and 1958, the south-western half of the station roof, and portions of its north-eastern half and the end screens were removed. The original glass panes were replaced by large patent glazing panels. The substantial supporting wall at the south-western side of the station was left in place. The wall is built of sandstone and linked to the main buildings by a series of arched tunnels in the undercroft.
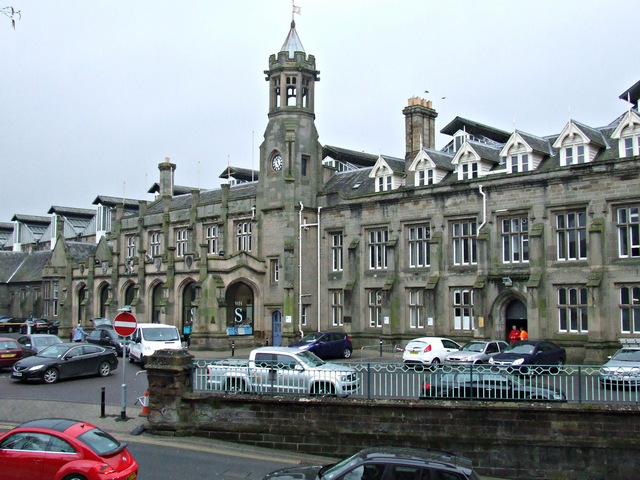
In November 1972, the station received Grade II* listed status; its citation notes: "The building by Tite is among the most important early major railway stations in Britain". In April 1994, the freestanding retaining wall was also listed separately as Grade II.
Restorations
Between October 2010 and March 2011, a series of improvements were performed at Carlisle Station, focused upon its passenger amenities, such as the waiting, meeting and seating areas. From 13 July 2013 to 7 April 2014, as part of a £1.5 million refurbishment project, accessibility at the station was improved via the refurbishment of the lifts and other alterations to achieve step-free access to all of the platforms. In conjunction, a formerly-disused subway was also renovated.
According to rail industry publication Rail Engineer, it was clear by 2014 that the station's roof was in need of restoration. The steel trusses were found to have been sagging in places, which was speculated to have been a result not only of the structure's age but also come as a consequence of the alterations performed during the 1950s, having been exacerbated by the adoption of rigid glazing and insufficient drainage systems. Multiple panels have cracked or broken, resulting in the deployment of several nets to catch falling glass, while rain water often pooled in areas of the roof rather than draining away. Furthermore, maintenance activities were complicated by a lack of access to the roof on the part of safety restrictions, preventing even routine cleaning, thus the panels were perpetually dirty and provided poor natural lighting conditions throughout the platforms.
During November 2015, work commenced upon the repair and refurbishment of the station's roof, as well as the rebuilding of all eight platforms under a £14.7 million scheme that was managed and carried out by national rail infrastructure management company Network Rail. This programme was planned by global design consulting firm Arcadis in close cooperation with both Historic England and Carlisle City Council; while the renovated roof was designed to incorporate modern elements and contemporary construction techniques, significant attention was reportedly paid to maintaining its historical aesthetic. The new roof is primarily composed of ethylene tetrafluoroethylene (EFTE) sheeting and aluminium frames, which is claimed to possess a high level of resistance to corrosion as well as retaining considerable strength and being far lighter than conventional glass panes; other benefits include the roof being shatter-proof and self-cleaning. Construction company Galliford Try served as the principal contractor performing the roof replacement, while Vector Foiltec manufactured and fitted the EFTE sheets. It was also decided to repaint the metalwork of the roof, which was not originally included in the programme's scope.
During February 2018, a second phase of this renovation programme, which was focused upon the platforms themselves, was scheduled to commence.
Accidents and incidents
- On 6 June 1961, a light engine and a freight train collided under the Caldewgate road bridge.
- On 1 May 1984, a runaway freight train collided with and destroyed the River Caldew bridge at Dentonholme. This incident directly contributed to the decision to permanently close the goods line shortly thereafter. However, the goods line was not dismantled; it has been speculated that it could be restored and re-opened to traffic one day, if the measure was to be deemed necessary for the relief of freight congestion in the vicinity of the station.
Facilities
The station is a fully staffed facility during normal hours; the booking office is typically manned each day from the start of services in the morning up until 20:00 in the evening. A number of ticket machines are also available in the booking hall, allowing tickets to be purchased even when the booking office is not in service. To the north of the station's portico, located directly between the main entrance and the station offices, is a square clock tower, furnished with an octagonal lantern; to the south of the portico are single-storey waiting and refreshment rooms. Interior details of these rooms included Tudor and Gothic-style fireplaces and linen-fold wood-panelled doors.
Multiple waiting rooms are located on both of the station's main platforms; additionally, there is a newsagents present upon the concourse and a buffet on platform three. Train running information is provided across the station in the form of auditory announcements over a public address system, along with a series of distributed digital display screens. In line with accessibility legislation, full step-free access is possible to all platforms on the station via ramps to the footbridge or lifts and subway.
Layout and services
Long-distance services are operated by Avanti West Coast, with the main routes being London Euston–Glasgow Central and Scotland–-London Euston and TransPennine Express Scotland-Manchester. Caledonian Sleeper passengers from/to London Euston may also alight/board here. Northern operate local stopping services to Newcastle Central via the Tyne Valley Line, to Barrow-in-Furness via the Cumbrian Coast Line, and to Leeds via the scenic Settle–Carlisle line. Abellio ScotRail also operate services to Glasgow Central via Dumfries and Kilmarnock. There are 8 platforms at the station in total – 3 through and 5 bays, organised as follows (from west to east):
- Platform 1: Relief West Coast Main Line platform (bi-directional) and occasional Caledonian Sleeper - this is the normal north-bound West Coast Main Line platform
- Platform 2: Cumbrian Coast Line bay
- Platform 3: West Coast Main Line north-bound platform (bi-directional), mostly TransPennine Express north-bound. Also Glasgow South Western line services originating from the Tyne Valley Line
- Platform 4: West Coast Main Line south-bound platform (bi-directional). Also Tyne Valley line services originating from the Glasgow South Western Line
- Platform 5 & 6: Tyne Valley Line bay/Carlisle to Leeds Line (Settle and Carlisle line) bay. These platforms often alternate
- Platform 7: Scottish services to various destinations between Carlisle and Glasgow via the Glasgow South Western Line
- Platform 8: Early morning services to Scotland
There are stabling roads between Platforms 3 and 4 in the train shed, and a loop around Platform 1. There are several electrified sidings to the west of Platform 1. There are substantial buildings on both the western island and the main up platform on the east side, with the main station buffet on the former and the travel centre/ticket office and shop on the latter. Both main platforms have waiting rooms and toilets and are linked by a fully accessible footbridge.
Freight trains formerly used a goods line to the west to bypass the station, but this was closed in 1984 after a runaway rake of container wagons derailed at high speed on the River Caldew bridge at Dentonholme, damaging it beyond economic repair. Nearly all freight services (apart from those running directly from the Cumbrian Coast Line toward the Tyne Valley Line or the Settle–Carlisle Line, or vice versa) now have to use one of the main platform lines when passing through the station, which can cause congestion at peak times.
2008
Service frequencies on each route varied – on Mondays to Saturdays there were trains every one or two hours to London and at least every hour to Birmingham, Glasgow and Edinburgh. First TransPennine Express operated seven trains per day to and there was a basic hourly service to both Newcastle and Whitehaven but a less frequent one to Glasgow via Kilmarnock (eight trains per day), to Leeds (six trains per day M–F, seven SO) and to Barrow-in-Furness (seven).
On Sundays the service was hourly on the WCML (every two hours to all main destinations apart from Manchester) and to Newcastle but infrequent on the other routes (three trains to Leeds and Whitehaven, two to Kilmarnock and another two to Dumfries only). There were two summer-only DalesRail afternoon trains to Preston via but no service to Barrow. By this time, the former CrossCountry services to such destinations as Cheltenham, Bristol, Plymouth, Southampton and Bournemouth had ceased.
2009
Service frequencies on the West Coast Main Line improved somewhat following the introduction of the new VHF timetable by Virgin Trains. From Mondays to Saturdays there were now trains every hour to London for much of the day (although one service from Euston no longer stopped here, running non-stop between Preston and Glasgow) and at least every hour to Birmingham, Glasgow and Edinburgh. First TransPennine Express operated seven trains per day to and there was a basic hourly service to both Newcastle and Whitehaven but a less frequent one to Glasgow via Kilmarnock (eight trains per day), to Leeds (seven per day Mon–Sat since the May 2011 timetable alterations) and to Barrow-in-Furness (eight).
On Sundays the service was hourly on the WCML (every two hours to all main destinations apart from Manchester) and to Newcastle but infrequent on the other routes (three trains to Leeds and Whitehaven, two to Kilmarnock and another two to Dumfries only). There were two summer-only DalesRail afternoon trains to Preston via but no service to Barrow.
2019
The following trains call at Carlisle:
Avanti West Coast
For most of the day Avanti West Coast operate:-
- One train per hour each way London Euston (direct route via Trent Valley) to Glasgow Central
- One train per hour each way London Euston via Birmingham to Glasgow Central alternating with Edinburgh Waverley. This through service was a major change from the start of the 2013–14 timetable when the hourly London Euston-Birmingham-Wolverhampton service was combined with the hourly Birmingham to Glasgow/Edinburgh service.
TransPennine Express
Provide an hourly service Manchester Airport to Edinburgh Waverley and Glasgow Central (alternating).
Abellio ScotRail
Provide the following service: Monday to Saturdays, There is an hourly service to Dumfries with a (mostly) 2-hourly service to Glasgow Central via Kilmarnock. Sundays: There are 5 trains per day to Dumfries with 2 of these trains going to Glasgow Central.
Northern
Northern provide the following service:
- One train per hour to Barrow (some afternoon & evening trains terminate at Whitehaven).
- Two trains per hour to Newcastle via Hexham (one per hour on Sundays), with extensions to Morpeth or Middlesbrough. Some are through services between Newcastle and Glasgow South Western line destinations (or vice versa) using Abellio ScotRail units
- Eight trains per day to Leeds via Settle.
- Two trains per day to Dumfries.
Since May 2018, there are now five trains to Leeds on Sundays (including one through to ) plus a single DalesRail service to via Preston. A Sunday service along the Cumbrian Coast line to Barrow also began at the summer 2018 timetable change (the first since 1976) - eight trains now run to Barrow, plus a further five to Whitehaven only.
London North Eastern Railway
London North Eastern Railway services call at Carlisle on a couple of weekends a year when the East Coast Main Line is closed for engineering work. They operate mainly hourly service to London King's Cross and Edinburgh Waverley.
Caledonian Sleeper
All Caledonian Sleeper services pass through Carlisle once a night except Saturdays (and engineering diversions) on their journey between London Euston and several Scottish destinations. Passengers may only board the London-bound service from Glasgow Central/Edinburgh Waverley, or only alight services in the opposite direction. Services from/to London Euston to/from Aberdeen, Inverness and Fort William run as a separate train that runs through Carlisle without a scheduled stop.
Adverse weather in 2015-16
All services toward Glasgow & Edinburgh over the WCML were suspended due to flood-related damage to the River Clyde bridge at Lamington (caused by Storm Frank). A limited number of trains to & from Glasgow were being diverted via Dumfries, whilst most others were replaced by express coaches. Repair work was initially expected to take at least 4 weeks to complete and services were not expected to restart over the structure until March 2016. Following better than expected weather conditions and delivery of key components earlier than planned, the work was completed ahead of schedule and trains resumed on 22 February 2016. This follows on from previous disruption caused by Storm Desmond on 5–6 December 2015 - flooding just north of the station at the bridge over the River Caldew led to a temporary suspension of services to and from Scotland and subsequent major delays to trains for more than two weeks.
Services towards Newcastle & Leeds were also disrupted at the same time due to weather-related landslips near and respectively. A replacement bus service ran between Hexham & whilst repairs were carried out on the Tyne Valley line. The line reopened to traffic on 8 February 2016. Services on the Settle line still ran initially, but as only one line was available between Cotehill and & capacity was therefore restricted, an emergency timetable was in operation with extended journey times and some trains being replaced by buses. Further ground movement at the landslip site at Eden Brows led to the suspension of all services as far south as Appleby on 9 February 2016, as Network Rail engineers deemed that it was no longer safe to operate trains over the affected portion of line. The line remained closed for over a year whilst the damaged embankment was underpinned and stabilised, and the track and formation repaired. Network Rail started work on the £23 million project to repair the embankment & formation in July 2016, with the line due to reopen on 31 March 2017. The line reopened as planned on that date, with the first train departing on schedule at 05:50 and a special excursion train hauled by the preserved steam locomotive Flying Scotsman visiting the station later in the day.
Citations
Sources
Visit the page: Carlisle railway station for references and further details. You can contribute to this article on Wikipedia.

from Geograph (geograph)
Lancaster and Carlisle Railway plaque on Carlisle station
Pinned by Simon Cotterill

Co-Curate Page
Settle and Carlisle Railway
- Overview About the Settle-Carlisle Line The Settle–Carlisle line (also known as the Settle and Carlisle (S&C)) is a main railway line in northern England. The route, which crosses the …

from Flickr (flickr)
CARLISLE c1910 Railway Station & Scotch Express - Real Photo
Pinned by Peter Smith

from Geograph (geograph)
Lancaster and Carlisle Railway plaque on Carlisle station
Pinned by Simon Cotterill

Co-Curate Page
Settle and Carlisle Railway
- Overview About the Settle-Carlisle Line The Settle–Carlisle line (also known as the Settle and Carlisle (S&C)) is a main railway line in northern England. The route, which crosses the …

from Flickr (flickr)
CARLISLE c1910 Railway Station & Scotch Express - Real Photo
Pinned by Peter Smith
List grade: 2*
Wikipedia: Carlisle railway st…
County: Cumbria
Grid ref: NY4023655540