Topics > Seaton
Seaton
Seaton in a village in the Allerdale district of Cumbria, located on the north side of the River Derwent, accross the river from Workington. Historically Seaton was part of the parish of Camerton in the county of Cumberland. Seaton Civil Parish was formed in 1894 and today has a population of around 5,000.
SEATON, a township, in the parish of Cammerton, union of Cockermouth, Allerdale ward below Derwent, W. division of Cumberland, 1¾ mile (N. E.) from Workington; containing 787 inhabitants. Here are extensive collieries and iron-works, near which the Derwent is crossed by a stone bridge, opposite to Workington. The tithes have been commuted for £295, payable to the Dean and Chapter of Carlisle; and there is a glebe of nearly 7 acres.
Extract from: A Topographical Dictionary of England comprising the several counties, cities, boroughs, corporate and market towns, parishes, and townships..... 7th Edition, by Samuel Lewis, London, 1848.
Seaton is a village and civil parish in west Cumbria. It is home to around 5,000 people and is one of the largest villages in England. The population of the parish was measured in the 2011 Census as 5,022. Historically a part of Cumberland, it is situated on the north side of the River Derwent, across from the town of Workington, and close to the smaller village of Camerton. Seaton forms part of the Borough of Allerdale.
Etymology
The name Seaton is believed to originate from the Old English name 'Sǣtūn'. where 'tūn' means 'homestead' or 'village', and 'sǣ' simply means 'sea'. However, since Seaton is over a mile away from the sea, this interpretation of the name is not certain.
History
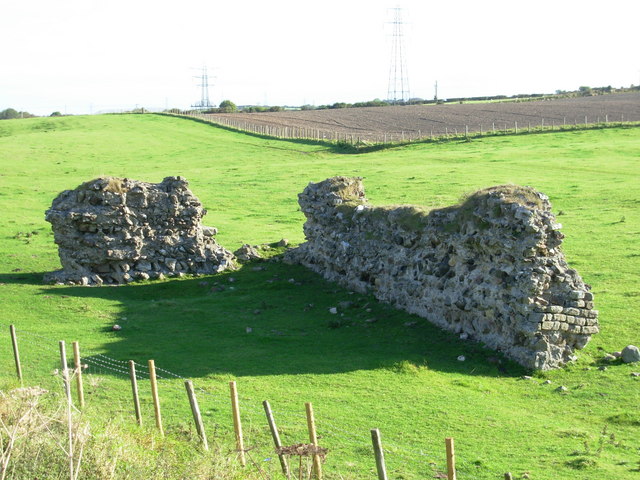
The earliest evidence of habitation in and around Seaton are the so-called 'Burrow Walls' less than a mile west of the village. These walls are the remains of a medieval manor house, itself built within the remains of a Roman fort believed to be called 'Magis'. It is believed the fort was built between 79 and 122 to guard the coast against attacks by the Scoti from Ireland and the Caledonii from Scotland.
Around 1100 the manor of Seaton was granted to a man named Orme on his marriage to Gunhild, sister of Waltheof, Lord of Allerdale and daughter of Gospatric, Earl of Northumbria. Orme's manor house was built on the same site as the old Roman fort, although a descendant, Patrick Culwen de Workington, pulled the house down and moved the family south across the river to Workington Hall. They would later adopt the surname Curwen, and generally used the title Lord of Workington, first obtained by Gospatric, son of Orme.
Traditionally, Seaton's economy was based on farming and mining. In 1762 Seaton Iron Works was established on the north bank of the River Derwent below the village at Barepot. It was a major concern at one time, employing hundreds of people, before its blast furnace ceased operation in 1857. The structures were demolished and there is very little trace remaining of the iron works today. The village experienced a large population increase during the 1800s caused by the boom of nearby Workington's steel industry. Workington's steel industry is now much smaller, and Seaton has become a dormitory settlement for other West Coast industries.
On 7 April 1964 Seaton was the site of the murder of John Alan West which led to the two final executions in the United Kingdom.
Governance
An electoral ward of the same name exists. This ward stretches east to Camerton with a total population of 5,196 at the 2011 Census.
Housing
The village is traditionally split into 'High' and 'Low' Seaton. Generally speaking, Low Seaton is the oldest part of the village and runs South West from Causeway Road towards Camerton. High Seaton makes up the remainder. Many housing estates have been built since 1950, including Ling Beck Park, Hunter's Drive Estate and Whitestiles, and house the vast majority of the current population. As these developments are in the north and east of the village, they are considered a part of High Seaton.
Amenities
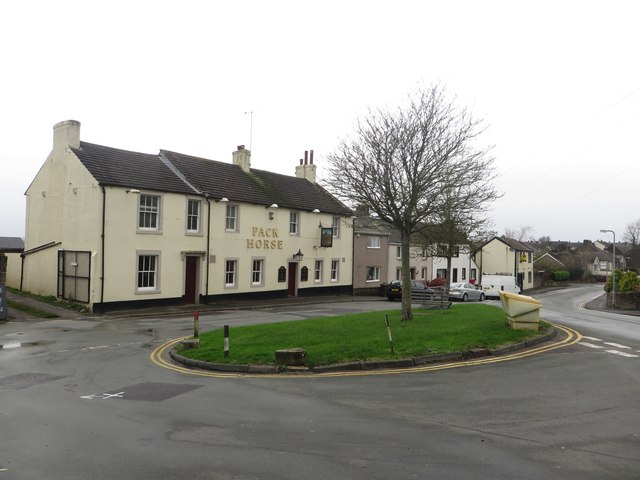
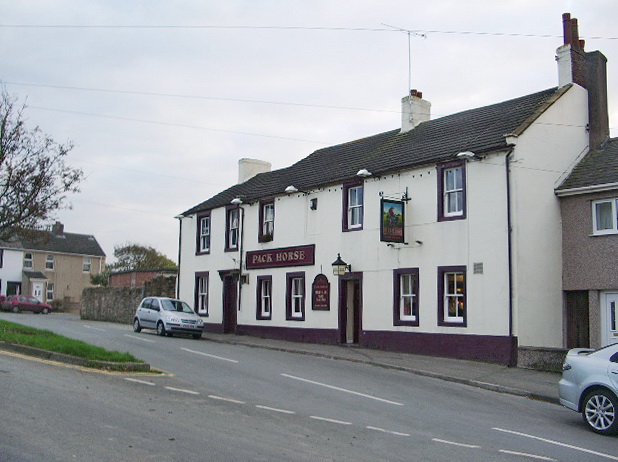
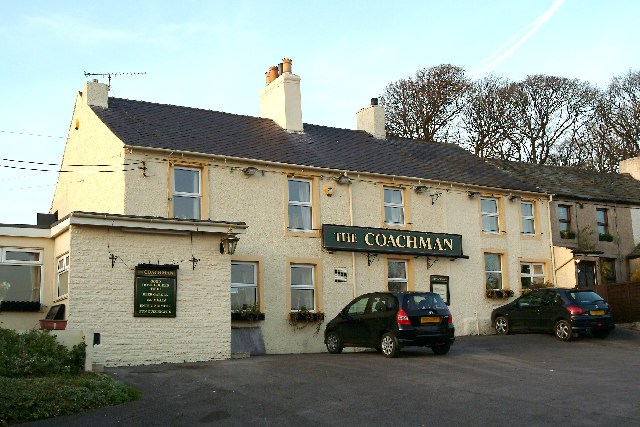
Amenities include: some small local shops, a petrol station, two schools – Seaton Academy (formerly Infant School), and Seaton Junior Church of England school, a library, three pubs, and a local Rugby league team, Seaton Rangers.
Parish Council
There are fifteen parish councillors in Seaton. The Parish Clerk is Paul Bramley. It meets in the Seaton Parish Rooms (on Church Road) on the 3rd Monday of every month. It has responsibility for planning applications, footpaths and other local amenities and has recently had grit bins placed at points around the village. Seaton Parish Council webpage
Transport
Seaton had a station on the Cleator and Workington Junction Railway, but the station closed in 1922.
Bus service number 47 links Seaton to Workington.
Visit the page: Seaton, Cumbria for references and further details. You can contribute to this article on Wikipedia.

from Flickr (flickr)
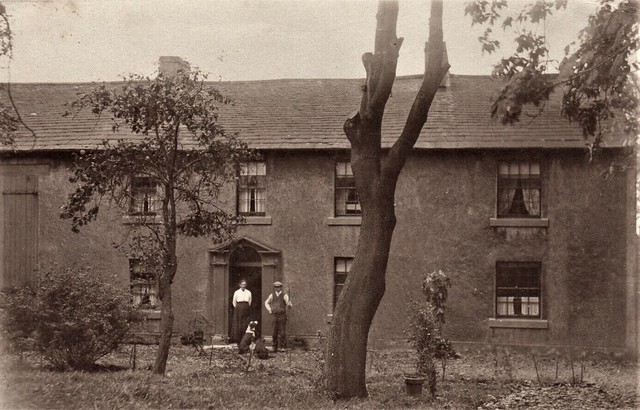
Sunnyside Seaton Workington RP pc used 1921 T S Lister X761
Pinned by Peter Smith

from Flickr (flickr)
Sunnyside Seaton Workington RP pc used 1921 T S Lister X761
Pinned by Peter Smith