Topics > County Durham > Durham (City) > Framwellgate Bridge
Framwellgate Bridge
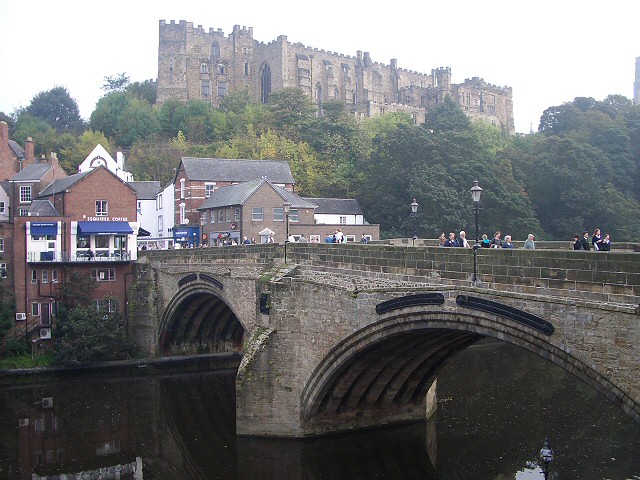
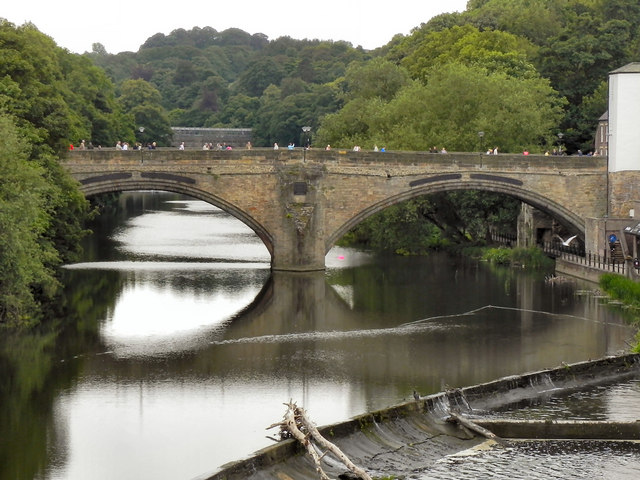
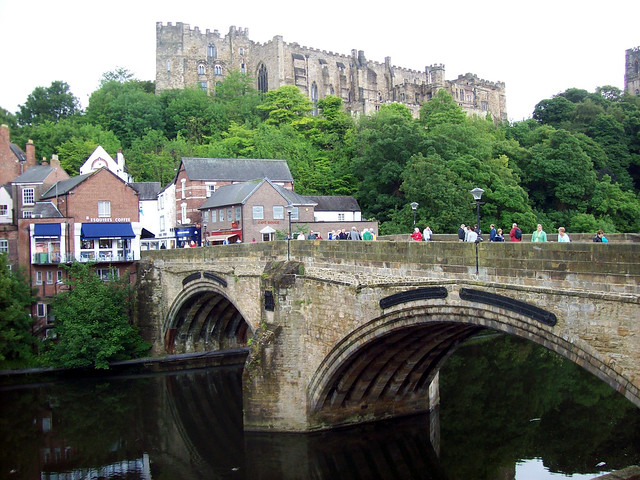
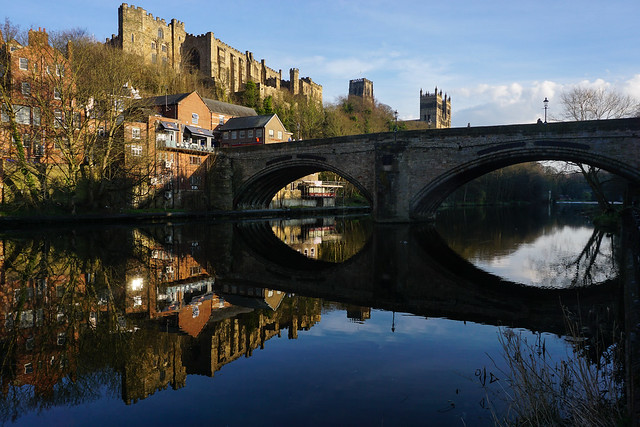
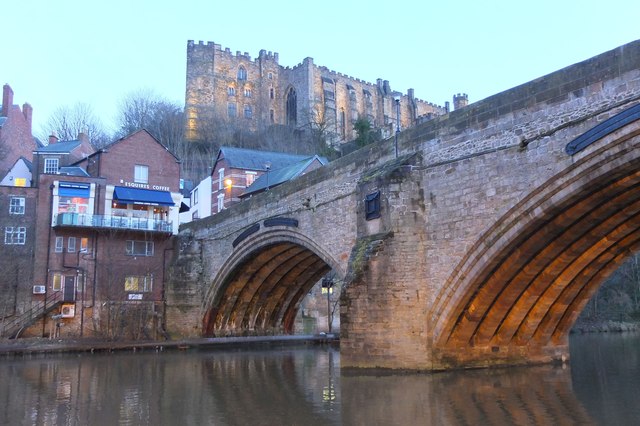
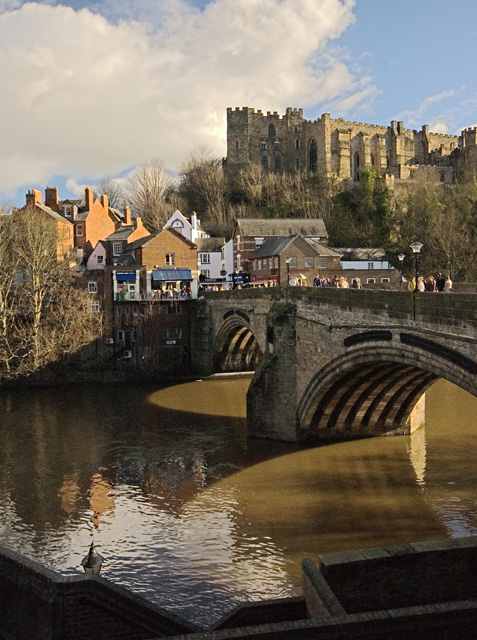
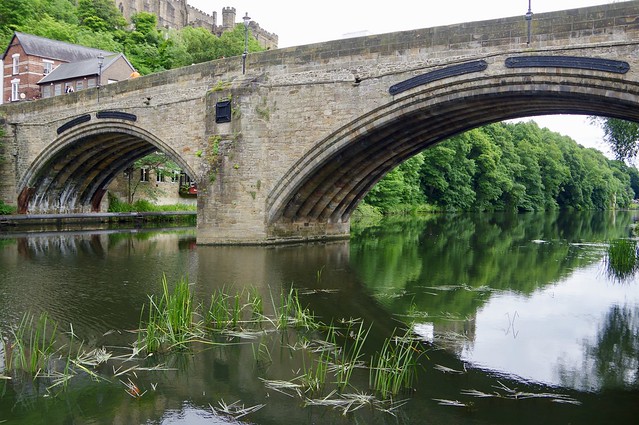
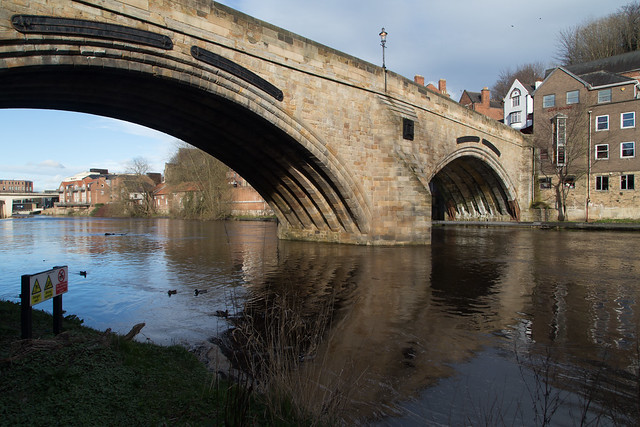
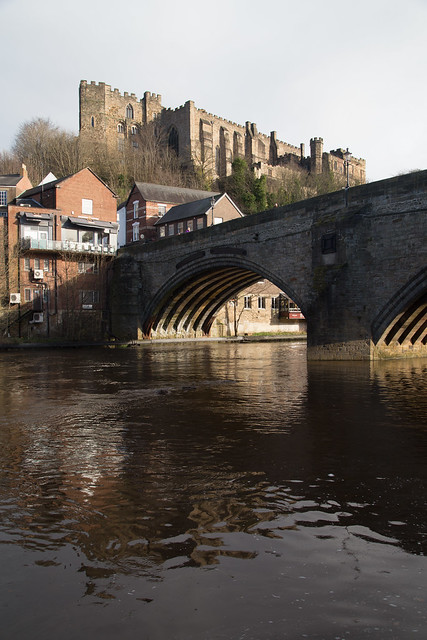
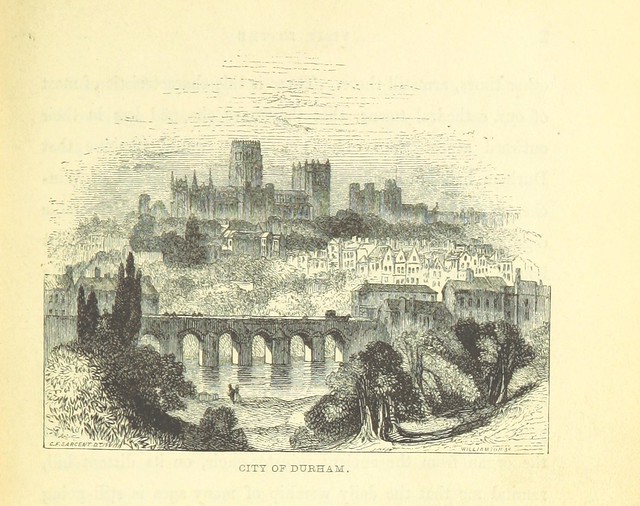
Framwellgate Bridge is a mediaeval masonry arch bridge across the River Wear, in Durham, England. It is Grade I listed on the National Heritage List for England.
History
The bridge was built after 1400 to replace one built early in the 12th century for Ranulf Flambard, who was Bishop of Durham 1099–1128. Flambard's bridge seems to have had five or six arches. A record of a lawsuit in 1437 records that Flambard's bridge:
...was broken by a flood during the Festival of the Nativity of the Blessed Virgin Mary in 1400.
Until the replacement bridge was completed a ferry was substituted, the profit from which was shared between the Bishop of Durham and the Prior of Durham Cathedral Priory.
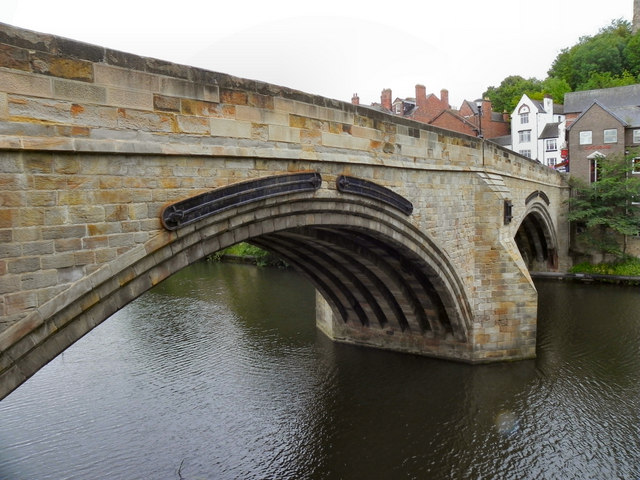
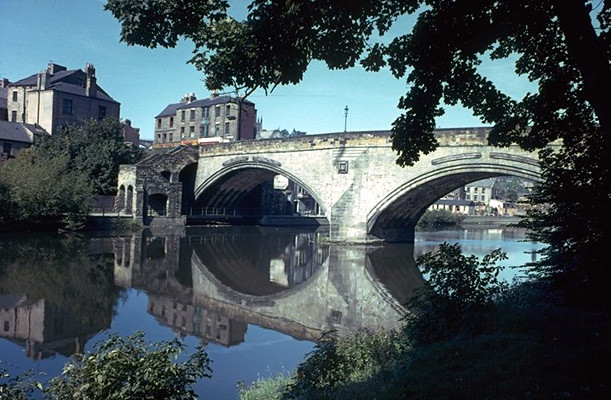
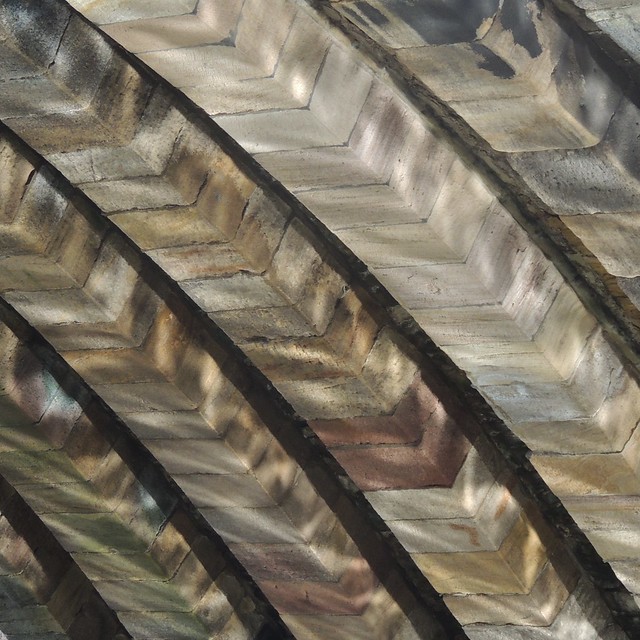
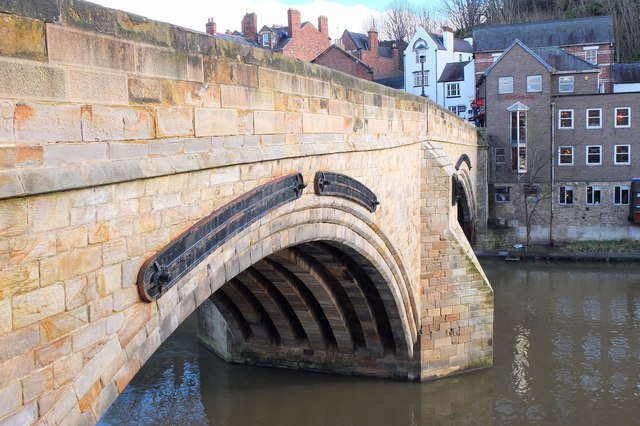
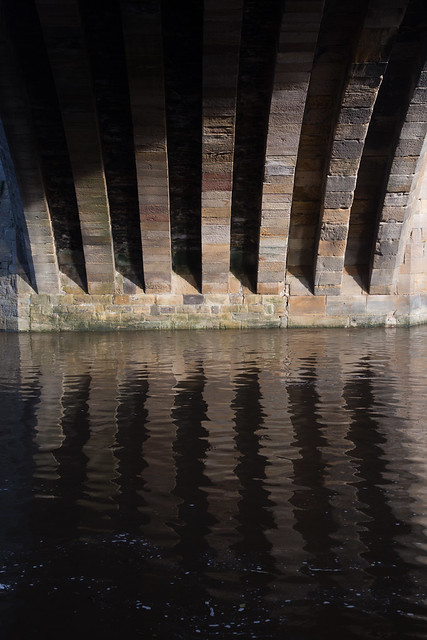
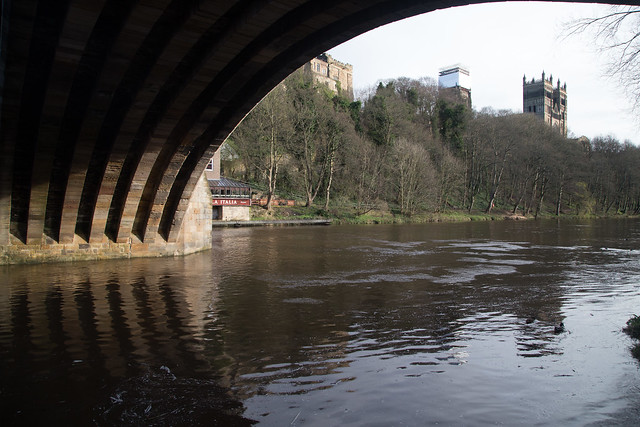
The current bridge is of two shallow arches, each with several reinforcing ribs. Their combined span is about . The early 16th-century antiquary John Leland recorded that there were three arches. A watercolour of Durham Cathedral painted by Thomas Girtin in 1799 shows a third arch, with a rounded shape characteristic of Norman architecture. Buildings at the central Durham end of the bridge may conceal the third arch, which may be a surviving part of Flambard's original 12th-century bridge.
Some sources indicate that both ends of bridge were fortified by towers and gates, though others infer only a single gatehouse was built on the peninsula side of the river. The gateway and tower at the eastern end of the bridge were deemed an obstruction to traffic and demolished in 1760. A flood destroyed two houses at the end of the bridge in 1771. Early in the 19th century the bridge was widened on its upstream side. It is now wide. Of the reinforcing ribs under each arch, five belong to the 15th-century bridge and two to the 19th-century widening.
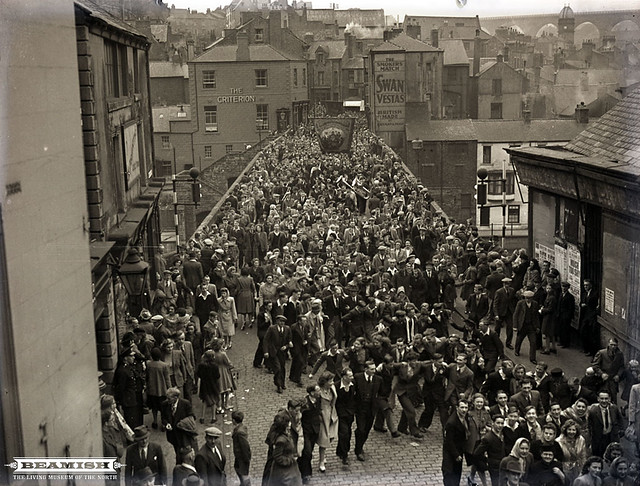
In 1318, Robert Neville, the "Peacock of the North", murdered his cousin, the Bishop's Steward, Sir Richard Fitzmarmaduke, at Framwellgate Bridge.
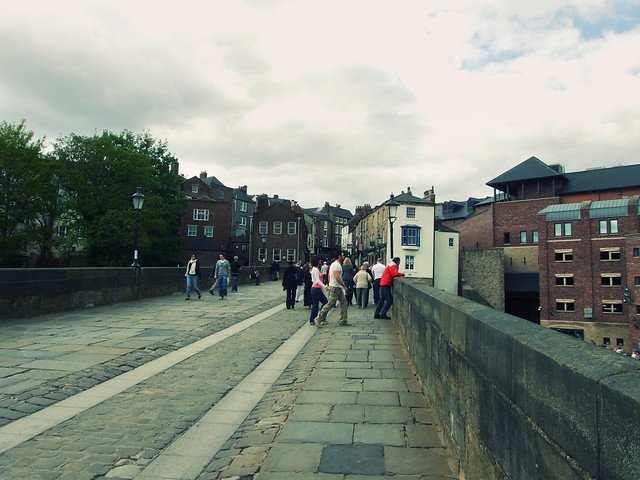
Until the building of Milburngate Bridge, in 1969, Framwellgate bridge was the main traffic route from the west through the centre of Durham. Today, the bridge is mainly pedestrianised, and only occasional service vehicles may use the bridge.
Visit the page: Framwellgate Bridge for references and further details. You can contribute to this article on Wikipedia.
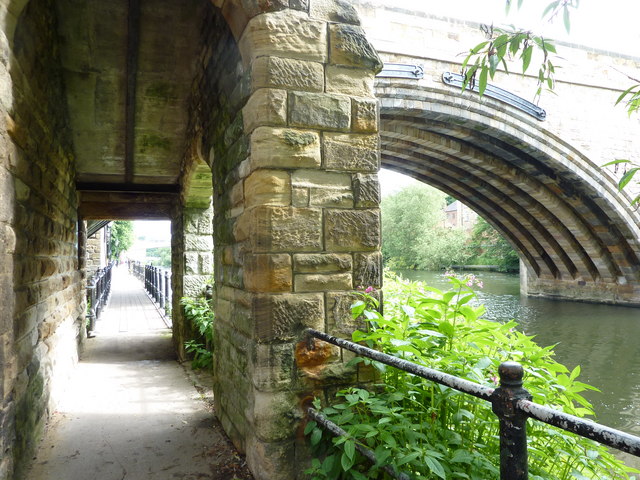

from Geograph (geograph)
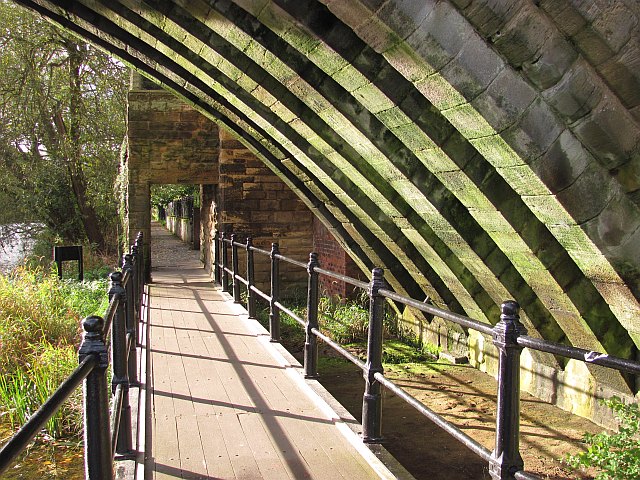
Footpath by the river Wear looking under Framwelgate Bridge.
Pinned by Simon Cotterill
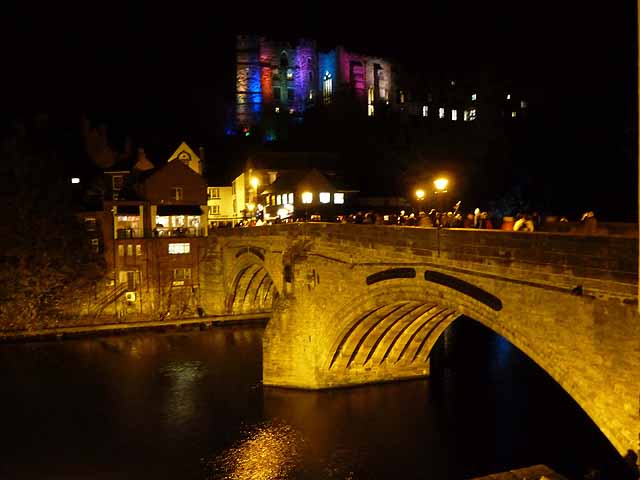

from Geograph (geograph)
Framwellgate Bridge and Durham Castle, Durham Lumiere 2011
Pinned by Simon Cotterill

from https://historicengland.org.u…
FRAMWELLGATE BRDGE - Durham - List Entry
- "Bridge. Early C15 replacement for early C12 bridge; widened early C19. Coursed squared sandstone with ashlar dressings: 2 wide elliptical arches on south side have 3 chamfers; central cutwater; iron …
Added by
Simon Cotterill

from Geograph (geograph)
Footpath by the river Wear looking under Framwelgate Bridge.
Pinned by Simon Cotterill

from Geograph (geograph)
Framwellgate Bridge and Durham Castle, Durham Lumiere 2011
Pinned by Simon Cotterill

from https://historicengland.org.u…
FRAMWELLGATE BRDGE - Durham - List Entry
- "Bridge. Early C15 replacement for early C12 bridge; widened early C19. Coursed squared sandstone with ashlar dressings: 2 wide elliptical arches on south side have 3 chamfers; central cutwater; iron …
Added by
Simon Cotterill
List number: 1322872
County: County Durham
Keys to the Past HER: D35206
Wikipedia: Framwellgate Bridge
Grid ref: NZ2723742431