Topics > Tyne and Wear > Sunderland > Springwell Village > Bowes Railway
Bowes Railway
Bowes Railway was originally built by George Stephenson in 1826 to transport coal from pits in north west Durham to boats on the River Tyne at Jarrow. The railway was bought by the Bowes family in 1850, who operated it until it was nationalised in 1947. Bowes Railway is the only preserved rope-hauled railway in the world. There is a museum at Springwell based around the original waggonshop and blacksmiths buildings and steam engines are operated by volunteer enthusiasts.
The Bowes Railway, built by George Stephenson in 1826, is the world's only operational preserved standard gauge cable railway system. It was built to transport coal from pits in Durham to boats on the River Tyne. The site is a Scheduled Ancient Monument. The railway is open the first weekend of each month (February - December) and every week Tuesday & Thursday for static display and guided tours. Plus a number of event days throughout the year. Entry is currently by donation.
History
Background
The Grand Allies, a partnership of businessmen including John Bowes, opened a colliery at Springwell in Durham. A railway was needed to transport the coal to the River Tyne. The plan was to build inclined planes and use a combination of steam power and gravity to move the coal wagons. The railway was designed by George Stephenson who built the Hetton colliery railway which was completed in 1822.
Construction
The railway was built between Mount Moor and Jarrow via Springwell village. The first section to open was between Springwell and Jarrow which opened on 17 January 1826, Mount Moor followed in April 1826. When the line opened it comprised four inclined planes: one steep incline from Mount Moor to Blackham's Hill, and one from Blackham's Hill to Springwell. At Blackham's Hill, the summit of both inclines, was the "hauler house", housing stationary engines to wind the ropes. A long self-acting incline ran from Springwell. Nearly of locomotive-worked line extended to Jarrow where a final incline served the coal staiths. The line was extended across the Team Valley to Kibblesworth Colliery in May 1842. The railway was completed in 1854 when a link from Marley Hill to Kibblesworth was connected enabling collieries in Dipton to be accessed.
Operation
From 1 January 1947 the railway was owned and operated by the National Coal Board. After 1974 no inclines remained working and the line was only worked north east of Wardley. The last day the inclines were used, Friday 4 October 1974, was filmed by BBC and Tyne -Tees TV crews.
What was left of the Bowes Railway north east of the inclines was served by a shed at Wardley. The line was reduced in length, until at the end there was only about in use, and it closed on 10 January 1986, a few days short of the 180th anniversary. This attenuated system the NCB called the Monkton Railways after the coke works that was its mainstay between 1975 and 1986.
Preserved railway
Tyne & Wear Industrial Monuments Trust was established April 1975 and took control of the line around Springwell from the National Coal Board through the medium of county council direction. By 1975 Springwell Workshops were building replica locomotives such as Locomotion No. 1 trading as Locomotion Enterprises. The Marley Hill shed of the Tanfield Railway is a former Bowes Railway running shed as are short lengths of the track at Marley Hill. Marley Hill became a preservation base from 1971.
The centre of the preserved Bowes Railway is Springwell Workshops.
A third Bowes Railway running shed at Wardley is the depot of the North East Bus Preservation Trust.
Rope Haulage
Original System
When the Bowes Railway was in full operation the line employed eight rope-worked inclined planes. Two of these (the Springwell and Birkheads inclines) were operated on the self-acting principle; the weight of descending full waggons hauled up the empty waggons via a rope running around a return wheel at the top of the hill. On the remaining six inclines (the Kibblesworth, Black Fell, Blackhams Hill East and West, Starrs and Allerdene Inclines) the ropes wre driven by a stationary steam or later electric haulage engine located at the incline top. This type of railway operation pre-dates modern locomotive- type operations and was laid down here by George Stephenson in 1826. The line's gradual closure eventually left only four inclines in use, these finally closing on 4 October 1974).
Preserved System
The line as preserved post-1974 includes two rope-worked inclines. These are the Blackhams Hill East and West inclines. Both are worked by the Blackhams Hill engine; this is a 300 h.p. Metropolitan Vickers engine commissioned on 30 July 1950. This works both the East or Flatt Incline (1170 yards at a gradient of 1 in 70) and the West or Short Bank (750 yards at a gradient 1 in 13). Over these inclines the preserved railway demonstrates one of the oldest and most unusual types of railway operation; it is now the only place in Britain where this can now be seen. However, the inclines are not currently operational, due to vandalism and decline.
Locomotives and brake vans
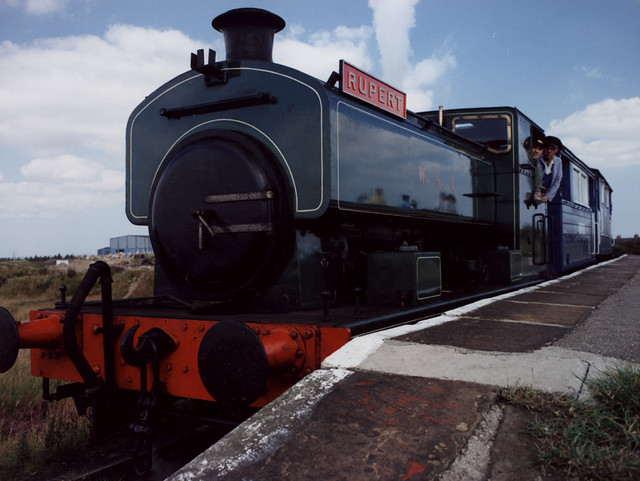
Steam locomotives
- Andrew Barclay 0-4-0ST W.S.T. makers Number 2361 built in 1954. Awaiting overhaul. Formerly used at Long Meg Mine and at Cocklakes.[12]
- Andrew Barclay 0-4-0ST No 22 (Number 6 Area B Group 85). makers number 2274 built in 1949, for use on the Bowes Railway. Awaiting overhaul.
- Peckett 0-4-0ST W6 Special Makers Number 1967 Merlin. Owned by the Merlin locomotive group, based at Bowes. Currently on loan to the Telford Steam Railway, Telford.
Diesel locomotives
- Planet 0-4-0 No 101. Used sometimes on shunting duties and freight trains but not as often as the Hunslet due to its small size.
- Hunslet Engine Company 0-4-0 No 6263. Used regularly on freight trains and shunting, the most powerful shunter on the line.
- Ruston & Hornsby Class 88 0-4-0 - Restored for use on both passenger and demonstration coal trains.
Brake vans
- Lambton Hetton & Joicey Collieries Brake van No 1. In use as a passenger vehicle on the trains.
- L.M.S. No 2, built for use in Derby. In use as a passenger vehicle on the trains.
- L.M.S. No 3 Brake van. In use as a passenger vehicle on the passenger trains.
Waggons
The railway also has a fleet of 45 original Bowes railway waggons dating from 1887 through to 1963, as well as seven similar waggons from other industrial sites in the North East.
The Railway Today
The museum is based around the workshops at Springwell, this contains the museums, shop, cafe, toilets and guided tours of the buildings dating back to 1826. The buildings such as the Waggonshop and blacksmiths are open during museum open days and guided tours can be arranged.
The site is open the first weekend of each month and every week Thursday, Friday and Saturday for static display and tours. Admission is free on non steaming days.
Visit the page: Bowes Railway for references and further details. You can contribute to this article on Wikipedia.

from Newcastle libraries (flickr)
578931:Bowes Railway Museum Gateshead unknown 1990
Pinned by Simon Cotterill

from Flickr (flickr)
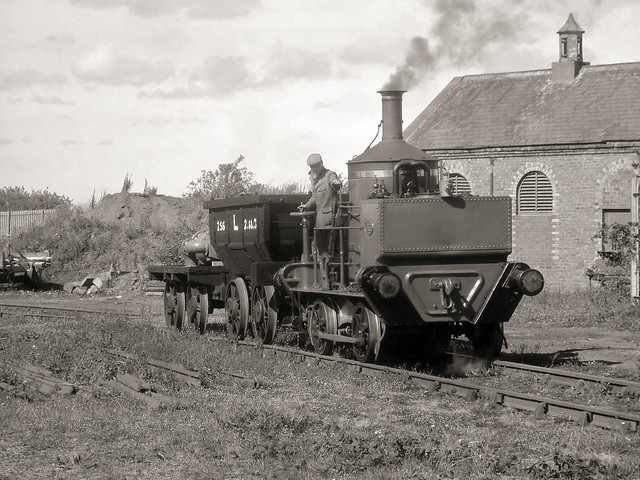
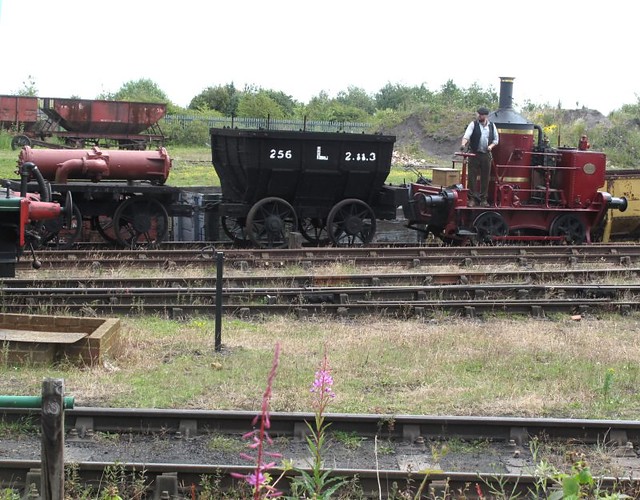
Steam hauled coal train on the Bowes Railway, Springwell
Pinned by Simon Cotterill

from Newcastle libraries (flickr)
578931:Bowes Railway Museum Gateshead unknown 1990
Pinned by Simon Cotterill

from Flickr (flickr)
Steam hauled coal train on the Bowes Railway, Springwell
Pinned by Simon Cotterill