Topics > County Durham > Durham (City) > Durham Castle
Durham Castle
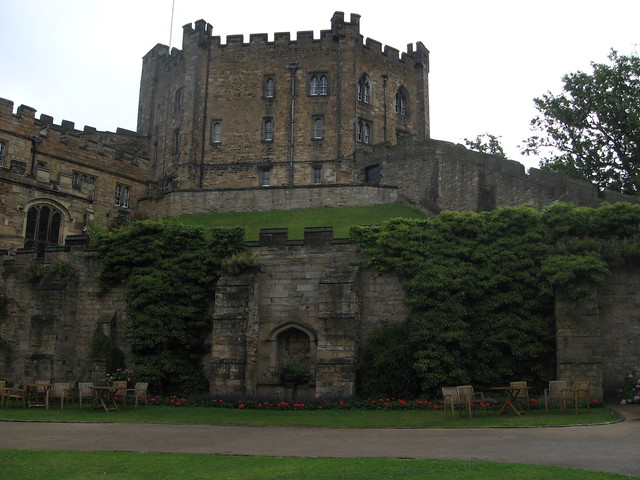
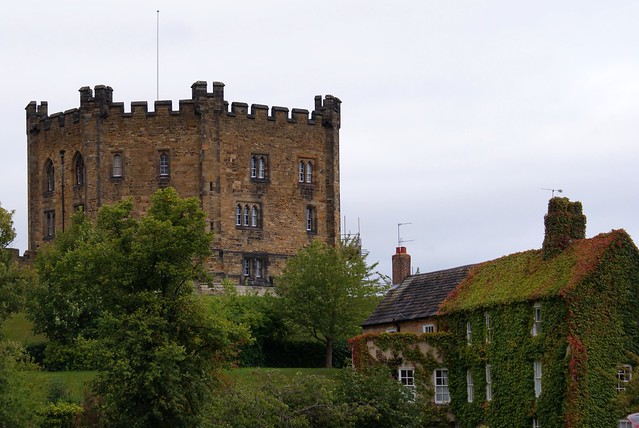
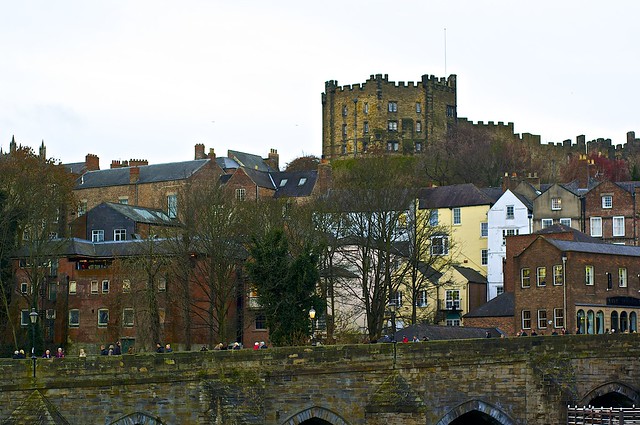
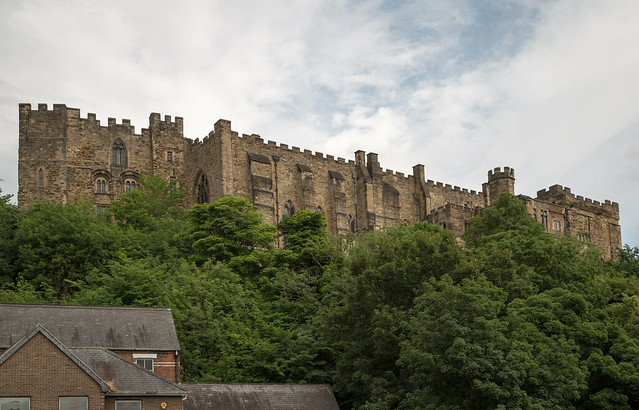
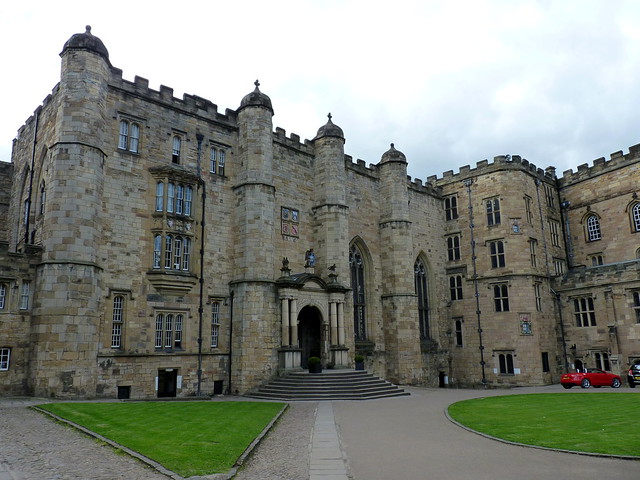
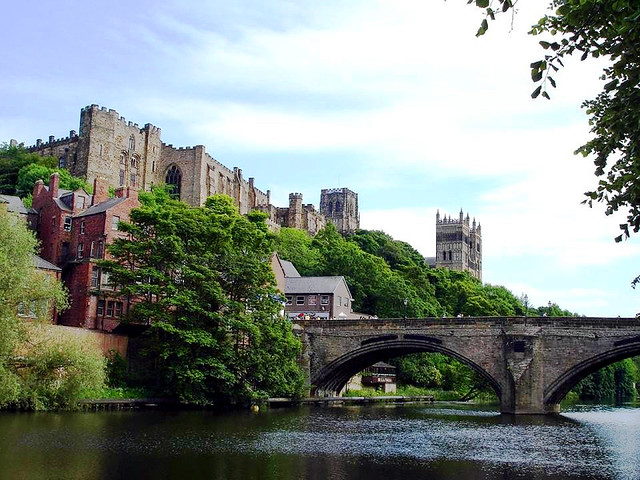
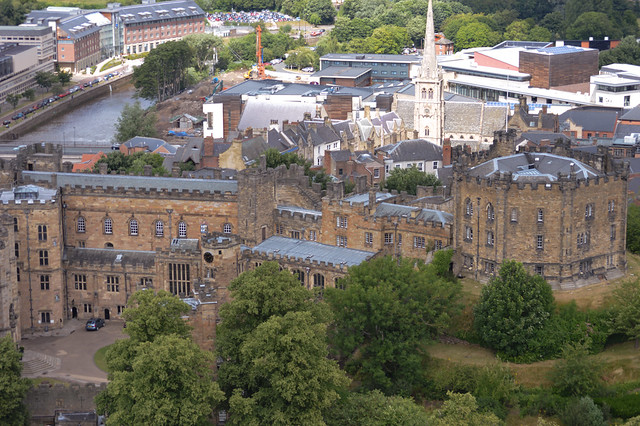
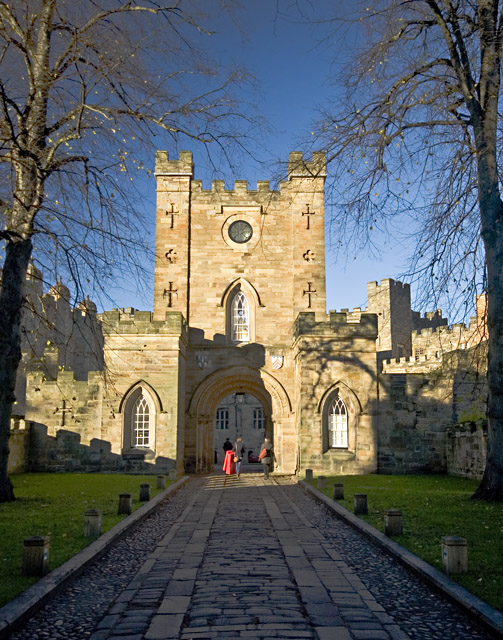
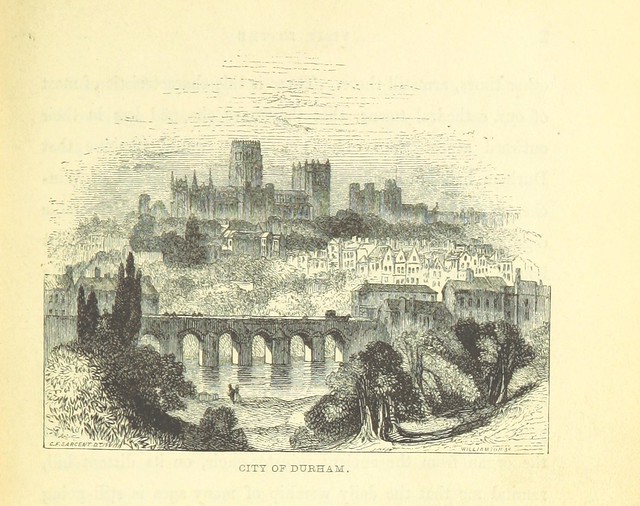
Durham Castle is a Norman castle in the city of Durham, England, which has been wholly occupied since 1840 by University College, Durham. It is open to the general public to visit, but only through guided tours, since it is in use as a working building and is home to over 100 students. The castle stands on top of a hill above the River Wear on Durham's peninsula, opposite Durham Cathedral .
History
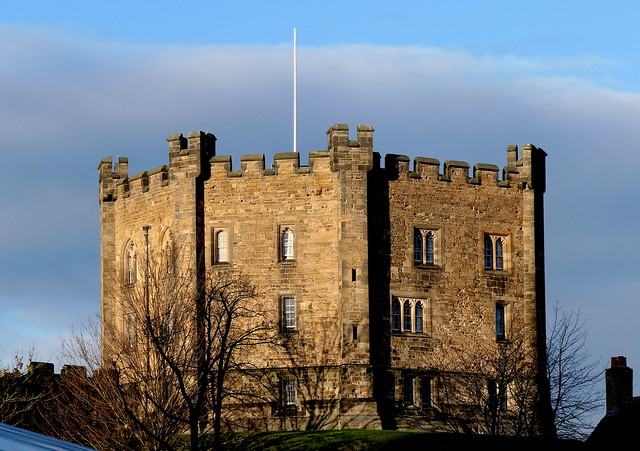
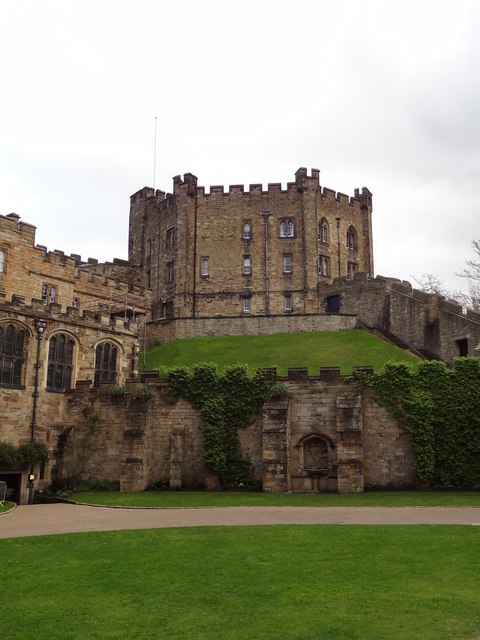
The castle was originally built in the 11th century as a projection of the Norman kings' power in the north of England, as the population of England in the north remained "wild and fickle" following the disruption of the Norman Conquest in 1066. It is an example of the early motte and bailey castles favoured by the Normans. The holder of the office of the Bishop of Durham was appointed by the King to exercise royal authority on his behalf, with the castle being his seat.
It remained the bishop's palace for the bishops of Durham until the bishops made Auckland Castle their primary residence and the castle was converted into a college.
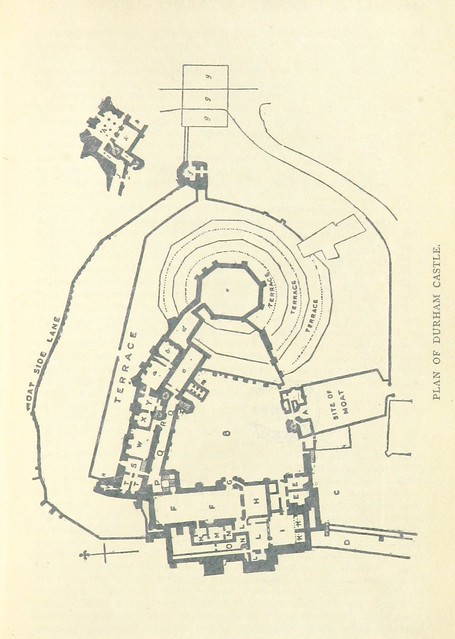
The castle has a large Great Hall, created by Bishop Antony Bek in the early 14th century. It was the largest Great Hall in Britain until Bishop Richard Foxe shortened it at the end of the 15th century. However, it is still high and over long.
University College
In 1837, the castle was donated to the newly formed University of Durham by Bishop Edward Maltby as accommodation for students. It was named University College. Architect Anthony Salvin rebuilt the dilapidated keep from the original plans. Opened in 1840, the castle still houses over 100 students, most of whom are in the keep.
Students and staff of the college eat their meals in Bishop Bek's Great Hall. The Great Hall's Undercroft, meanwhile, serves as the Junior Common Room, including its bar - i.e. as the principal common room for the college's undergraduate members. The two chapels are still used, both for services and other purposes such as theatrical performances. Other facilities contained within the castle include the college's library, the college offices, and the college's IT suite. During university vacations, the college offers rooms in the castle for (usually academic) conferences and as hotel accommodation. Access to the castle for the public is restricted to guided tours. Outside of these, only members of the college or vacation guests may visit the castle. In 2011, the castle was closed to guided tours whilst refurbishments were carried out. It reopened to the general public in the Autumn of 2011.
Chapels
The college makes extensive use of the castle's two chapels: the Norman Chapel, built around 1078, and Tunstall's Chapel, built in 1540.
The Norman Chapel is the oldest accessible part of the castle. Its architecture is Anglian in nature, possibly due to forced Anglian labour being used to build it. In the 15th century, its three windows were all but blocked up because of the expanded keep. It thus fell into disuse until 1841 when it was used as a corridor through which to access the keep. During the Second World War, it was used as a command and observation post for the Royal Air Force when its original use was recognised. It was re-consecrated shortly after the war and is still used for weekly services by the college.
Tunstall's Chapel is the more heavily used of the chapels, being somewhat larger. Bishop Cosin and Bishop Crewe extended it in the late 17th century. At the back of the chapel, some of the seats are 16th-century misericords (literally, mercy seats). These were designed such that a person standing for long periods of time could rest on a ledge of the upturned seat.
World Heritage Site
Durham Castle is jointly designated a UNESCO World Heritage Site with Durham Cathedral, a short distance across Palace Green.
Visit the page: Durham Castle for references and further details. You can contribute to this article on Wikipedia.
from Flickr (flickr)
Image taken from page 189 of 'Comprehensive Guide to the County of Durham. With maps and plans'
Pinned by Simon Cotterill
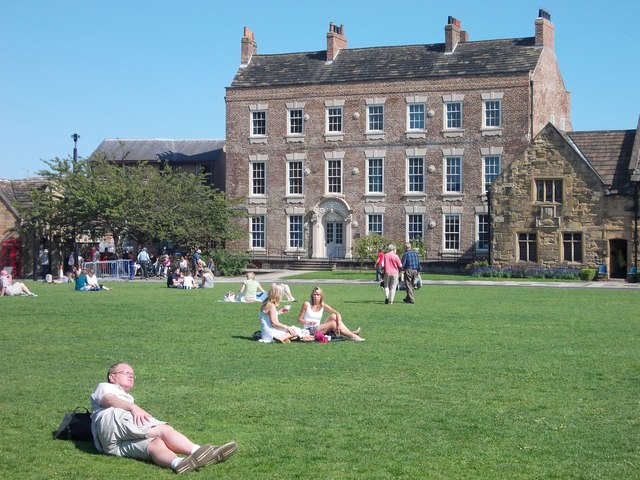

Co-Curate Page
Palace Green
- Overview About Palace Green Map Street View Palace Green is a grassed area immediately north of Durham Cathedral. The Green is surrounded by historic buildings, many associated with the Prince Bishops …

from Flickr (flickr)
Image taken from page 189 of 'Comprehensive Guide to the County of Durham. With maps and plans'
Pinned by Simon Cotterill