Maryport (Alavna) Roman fort, part of the Roman frontier defences along the Cumbrian coast, its associated vicus and a length of Roman road - List Entry

-
Description
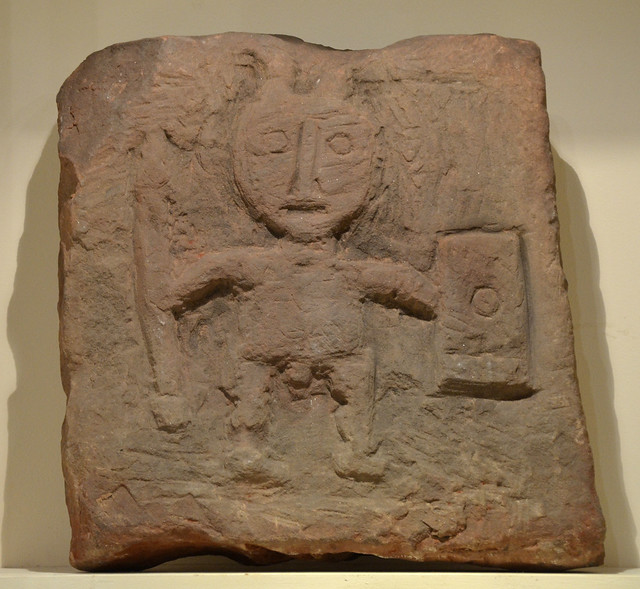
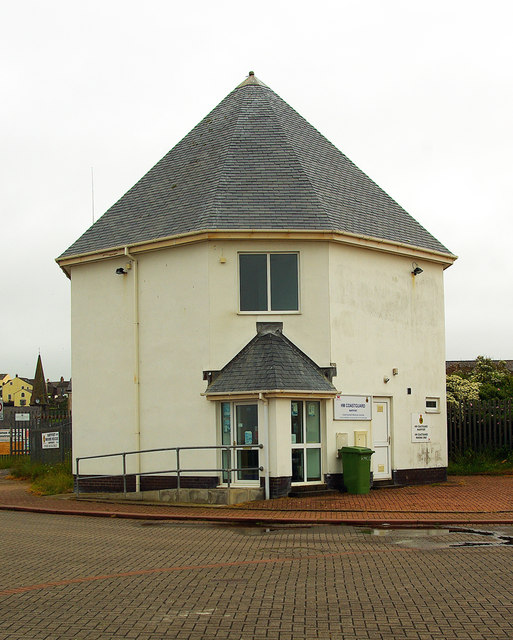
"....The monument includes the earthworks and buried remains of Maryport Roman fort - identified as the site of Alavna noted in classical sources - together with the buried remains of a large part of its associated vicus or civilian settlement. The vicus has been identified by a combination of antiquarian investigation and aerial photography. The vicus is located to the north and north east of the fort and includes a 420m length of Roman road running from the north gate of the fort through it. The fort formed part of the second century AD Roman frontier defences of forts, milefortlets and towers set approximately one third of a Roman mile apart along the vulnerable low-lying coastal plain of north west Cumbria and augmented in places by palisade fences. The monument is located on a sandstone ridge between 45m-56m OD close to the cliff edge from where there are extensive views in all directions but particularly out to sea and across the Solway Firth towards south western Scotland...." -
Owner
Historic England -
Source
Local (Co-Curate) -
License
What does this mean? Unknown license check permission to reuse
-
Further information
Link: https://historicengland.org.uk/listing/the-list/list-entry/1015415
Resource type: Text/Website
Added by: Simon Cotterill
Last modified: 4 years, 6 months ago
Viewed: 772 times
Picture Taken: Unknown -
Co-Curate tags