Topics > Transport and Travel > Railway > Locomotives > Locomotion No. 1
Locomotion No. 1
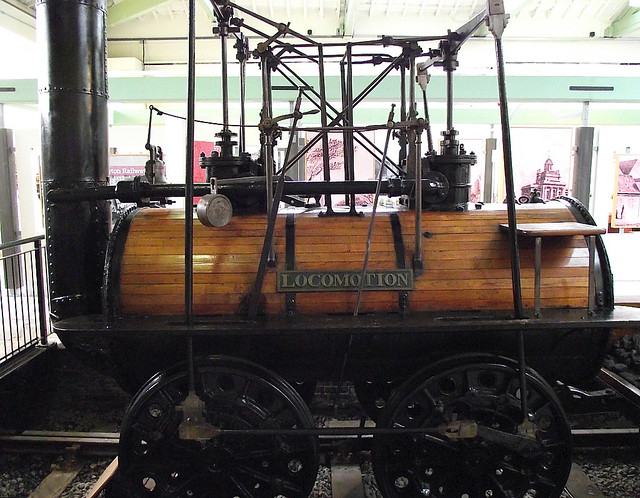
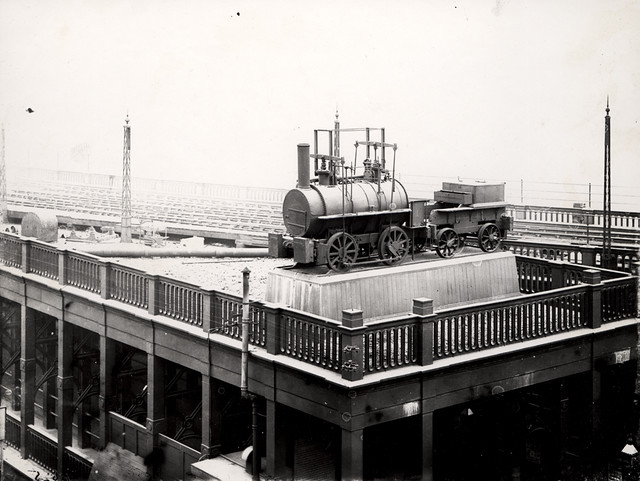
Locomotion No. 1 (originally named Active) is the first steam locomotive to carry passengers on a public rail line, the Stockton and Darlington Railway. Built by George and Robert Stephenson's company Robert Stephenson and Company in 1825.
Design
Locomotion used all the improvements that George Stephenson had pioneered in the Killingworth locomotives. It used high-pressure steam from a centre-flue boiler, with a steam-blast in the chimney, to drive two vertical cylinders, enclosed within the boiler. A pair of yokes above them transmitted the power downwards, through pairs of connecting rods. It made use of a loose eccentric valve gear, and was the first locomotive to use coupling rods to link its driving wheels together, rather than through a chain or gears. Because of the single flue, it had a poor heating surface compared to later steam locomotives. It had a top speed of .
This locomotive is historically important as the first to run on a public railway, rather than for the innovations in its design. It hauled the first train on the Stockton and Darlington Railway in north-east England on 27 September 1825.
On 1 July 1828, the boiler exploded at station, killing the driver John Cree. With advances in design such as those incorporated into Robert Stephenson's Rocket, Locomotion became obsolete very quickly. It was rebuilt and remained in service until 1841 when it was turned into a stationary engine.
Preservation
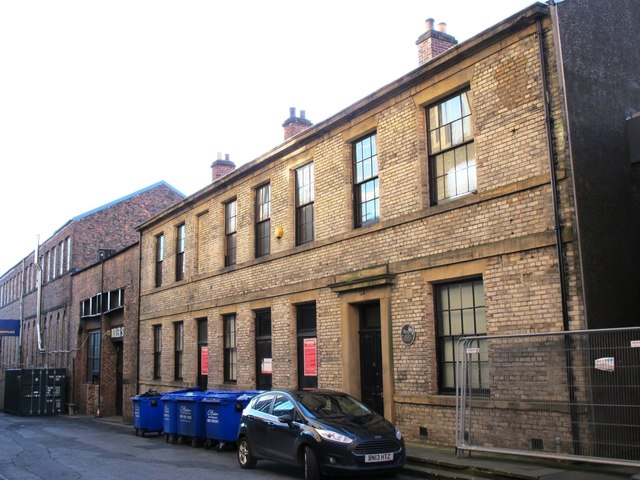
In 1857 it was preserved. Locomotion No. 1 was on display in Alfred Kitching's workshop near Hopetown Carriage Works from 1857 to the 1880s. From 1892 to 1975 it was on display along with Derwent on one of the platforms at Darlington's main station, Bank Top. The locomotive is currently on display at the Darlington Railway Centre and Museum, now known as Head of Steam, in the same building as Darlington's North Road station. Locomotion is on long-term loan from the National Railway Museum and is part of the National Collection.
There is a working replica of the locomotive at Beamish Museum which was built in 1975.
Visit the page: Locomotion No. 1 for references and further details. You can contribute to this article on Wikipedia.

from Flickr (flickr)
Stockton & Darlington Railway 0-4-0 No. 1 'Locomotion' (1825) Head of Steam, Darlington 30.06.2009 P6300109
Pinned by Simon Cotterill

from Flickr (flickr)
Stockton & Darlington Railway 0-4-0 No. 1 'Locomotion' (1825) Head of Steam, Darlington 30.06.2009 P6300119
Pinned by Simon Cotterill

Co-Curate Page
Stockton and Darlington Railway
- Overview Early History The Stockton and Darlington Railway was the world's first public railway to use steam locomotives. The railway was primarily built to transport coal from collieries around Shildon, …

Co-Curate Page
Stephenson Works
- Overview Map Street View In 1823, George Stephenson, his son Robert Stephenson, and partners, opened the world’s first purpose built locomotive works on Forth Banks (entrance on South Street). The "Locomotion", "Rocket", and "Planet" were …

from Flickr (flickr)
Stockton & Darlington Railway 0-4-0 No. 1 'Locomotion' (1825) Head of Steam, Darlington 30.06.2009 P6300109
Pinned by Simon Cotterill

from Flickr (flickr)
Stockton & Darlington Railway 0-4-0 No. 1 'Locomotion' (1825) Head of Steam, Darlington 30.06.2009 P6300119
Pinned by Simon Cotterill

Co-Curate Page
Stockton and Darlington Railway
- Overview Early History The Stockton and Darlington Railway was the world's first public railway to use steam locomotives. The railway was primarily built to transport coal from collieries around Shildon, …