Topics > People in History > John Smeaton (1724 - 1792)
John Smeaton (1724 - 1792)
John Smeaton (1724 - 1792) was a prominent engineer, considered to be a 'founding father' of British civil engineering. He designed bridges, canals, harbours, water and wind powered mills, and lighthouses around the country. This page links to some of his works in the North East and Cumbria.
John Smeaton (8 June 1724 – 28 October 1792) was a British civil engineer responsible for the design of bridges, canals, harbours and lighthouses. He was also a capable mechanical engineer and an eminent physicist. Smeaton was the first self-proclaimed "civil engineer", and is often regarded as the "father of civil engineering". He pioneered the use of hydraulic lime in concrete, using pebbles and powdered brick as aggregate. Smeaton was associated with the Lunar Society.
Law and physics
Smeaton was born in Austhorpe, Leeds, England. After studying at Leeds Grammar School he joined his father's law firm, but left to become a mathematical instrument maker (working with Henry Hindley), developing, among other instruments, a pyrometer to study material expansion. In 1750, his premises were in the Great Turnstile in Holborn.
He was elected a Fellow of the Royal Society in 1753 and in 1759 won the Copley Medal for his research into the mechanics of waterwheels and windmills. His 1759 paper "An Experimental Enquiry Concerning the Natural Powers of Water and Wind to Turn Mills and Other Machines Depending on Circular Motion" addressed the relationship between pressure and velocity for objects moving in air (Smeaton noted that the table doing so was actually contributed by "my friend Mr Rouse" "an ingenious gentleman of Harborough, Leicestershire" and calculated on the basis of Rouse's experiments), and his concepts were subsequently developed to devise the 'Smeaton Coefficient'. Smeaton's water wheel experiments were conducted on a small scale model with which he tested various configurations over a period of seven years. The resultant increase in efficiency in water power contributed to the Industrial Revolution.
Over the period 1759–1782 he performed a series of further experiments and measurements on water wheels that led him to support and champion the vis viva theory of German Gottfried Leibniz, an early formulation of conservation of energy. This led him into conflict with members of the academic establishment who rejected Leibniz's theory, believing it inconsistent with Sir Isaac Newton's conservation of momentum.
Smeaton coefficient
In his 1759 paper "An Experimental Enquiry Concerning the Natural Powers of Water and Wind to Turn Mills and Other Machines Depending on Circular Motion" Smeaton developed the concepts and data which became the basis for the Smeaton coefficient, the lift equation used by the Wright brothers. It has the form:
:L = k V^2 A C_l \,
where:
:L is the lift
:k is the Smeaton coefficient (see note below)
:V is the velocity
:A is the area in square feet
:C_l is the lift coefficient (the lift relative to the drag of a plate of the same area)
The Wright brothers determined with wind tunnels that the Smeaton coefficient value of 0.005 was incorrect and should have been 0.0033. In modern analysis, the lift coefficient is normalised by the dynamic pressure instead of the Smeaton coefficient.
Civil engineering
Smeaton is important in the history, rediscovery of, and development of modern cement, identifying the compositional requirements needed to obtain "hydraulicity" in lime; work which led ultimately to the invention of Portland cement. Portland cement led to the re-emergence of concrete as a modern building material, largely due to Smeaton's influence.
Recommended by the Royal Society, Smeaton designed the third Eddystone Lighthouse (1755–59). He pioneered the use of 'hydraulic lime' (a form of mortar that will set under water) and developed a technique involving dovetailed blocks of granite in the building of the lighthouse. His lighthouse remained in use until 1877 when the rock underlying the structure's foundations had begun to erode; it was dismantled and partially rebuilt at Plymouth Hoe where it is known as Smeaton's Tower.
Deciding that he wanted to focus on the lucrative field of civil engineering, he commenced an extensive series of commissions, including:
- the Calder and Hebble Navigation (1758–70)
- Coldstream Bridge over the River Tweed (1763–66)
- Improvements to the River Lee Navigation (1765–70)
- Smeaton's Pier in St Ives, Cornwall (1767–70)
- Perth Bridge over the River Tay in Perth (1766–71)
- Ripon Canal (1766–1773)
- Smeaton's Viaduct, which carries the A616 road (part of the original Great North Road) over the River Trent between Newark and South Muskham in Nottinghamshire (1768–70)
- the Forth and Clyde Canal from Grangemouth to Glasgow (1768–77)
- Langley on Tyne smelt mill, with Nicholas Walton, acting as receivers to the Greenwich Hospital, London (1768)
- Banff harbour (1770–75)
- Aberdeen bridge (1775–80)
- Peterhead harbour (1775–1881)
- Nent Force Level (1776–77)
- Harbour works at Ramsgate (retention basin 1776–83; jetty 1788–1792)
- Hexham bridge (1777–90)
- the Birmingham and Fazeley Canal (1782–89)
- St Austell's Charlestown harbour in Cornwall (1792)
Smeaton is considered to be the first expert witness to appear in an English court. Because of his expertise in engineering, he was called to testify in court for a case related to the silting-up of the harbour at Wells-next-the-Sea in Norfolk in 1782. He also acted as a consultant on the disastrous 63-year-long New Harbour at Rye, designed to combat the silting of the port of Winchelsea. The project is now known informally as "Smeaton's Harbour", but despite the name his involvement was limited and occurred more than 30 years after work on the harbour commenced. It closed in 1839.
Mechanical engineer
Employing his skills as a mechanical engineer, he devised a water engine for the Royal Botanic Gardens at Kew in 1761 and a watermill at Alston, Cumbria in 1767 (he is credited by some with inventing the cast-iron axle shaft for water wheels). In 1782 he built the Chimney Mill at Spital Tongues in Newcastle upon Tyne, the first 5-sailed smock mill in Britain. He also improved Thomas Newcomen's atmospheric engine, erecting one at Chacewater mine, Wheal Busy, in Cornwall in 1775.
In 1789 Smeaton applied an idea by Denis Papin, by using a force pump to maintain the pressure and fresh air inside a diving bell. This bell, built for the Hexham Bridge project, was not intended for underwater work, but in 1790 the design was updated to enable it to be used underwater on the breakwater at Ramsgate Harbour. Smeaton is also credited with explaining the fundamental differences and benefits of overshot versus undershot water wheels. Smeaton experimented with the Newcomen steam engine and made marked improvements around the time James Watt was building his first engines ().
Legacy
Smeaton died after suffering a stroke while walking in the garden of his family home at Austhorpe, and was buried in the parish church at Whitkirk, West Yorkshire. His surviving daughters erected a memorial to him and his wife, which is on the chancel wall of the church.
He is highly regarded by other engineers, having contributed to the Lunar Society and founded the Society of Civil Engineers in 1771. He coined the term civil engineers to distinguish them from military engineers graduating from the Royal Military Academy at Woolwich. The Society was a forerunner of the Institution of Civil Engineers, established in 1818, and was renamed the Smeatonian Society of Civil Engineers in 1830. His pupils included canal engineer William Jessop and architect and engineer Benjamin Latrobe.
The pioneering constant of proportionality describing pressure varying inversely as the square of the velocity when applied to objects moving in air was named Smeaton's coefficient in his honor. Based on his concepts and data, it was used by the Wright brothers in their pursuit of the first successful heavier-than-air aircraft.
Between 1860 and 1894 the design of the reverse side of the old penny coin showed (behind Britannia) a depiction of Smeaton’s Eddystone lighthouse.
Smeaton is one of six civil engineers depicted in the Stephenson stained glass window, designed by William Wailes and unveiled in Westminster Abbey in 1862. A memorial stone commemorating Smeaton himself was unveiled in the Abbey on 7 November 1994, by Noel Ordman, President of the Smeatonian Society of Civil Engineers.
John Smeaton Academy, a secondary school in the suburbs of Leeds adjacent to the Pendas Fields estate near Austhorpe, is named after Smeaton. He is also commemorated at the University of Plymouth, where the Mathematics and Technology Department is housed in a building named after him. A viaduct in the final stage of the Leeds Inner Ring Road, opened in 2008, was named after him.
In 2003 Smeaton was named among the top 10 technological innovators in Human Accomplishment: The Pursuit of Excellence in the Arts and Sciences, 800 B.C. to 1950. He is mentioned in the song "I Predict a Riot" (as a symbol of a more dignified and peaceful epoch in Leeds history; and in reference to a Junior School House at Leeds Grammar School, which lead singer Ricky Wilson attended) by the indie rock band Kaiser Chiefs, who are natives of Leeds.
Works
- Experimental enquiry concerning the natural powers of wind and water to turn mills and other machines depending on a circular motion. Paris: Louis Courcier. 1810.
Visit the page: John Smeaton for references and further details. You can contribute to this article on Wikipedia.

from https://commons.wikimedia.org…
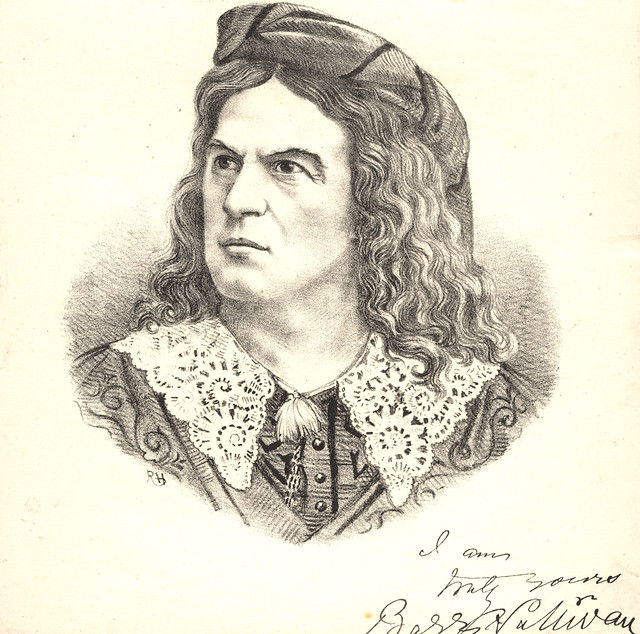
Portrait of John Smeaton
- c.1799 Public domain image c/o Wikimedia Commons. Portrait from The Royal Society.
Added by
Simon Cotterill

Co-Curate Page
Coldstream Bridge
- Overview About Coldstream Bridge Map Street View Coldstream Bridge, linking Coldstream, Scottish Borders with Cornhill-on-Tweed, Northumberland, is an 18th-century Grade II* listed bridge between England and Scotland, across the …

Co-Curate Page
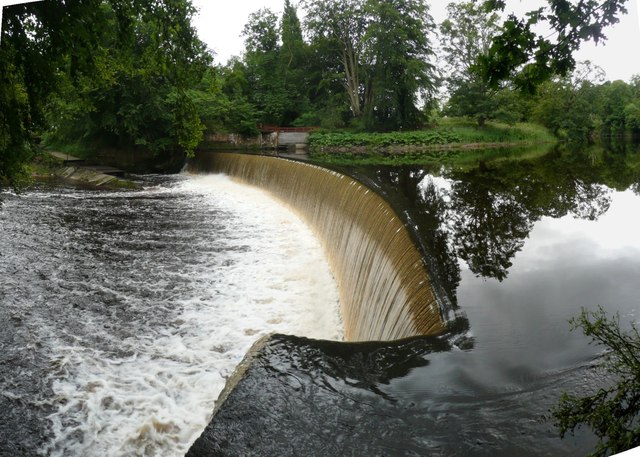
Dam on the River Coquet
- Overview Map This horseshoe-shaped dam on the River Coquet was built in 1775 to provide water power for Park Mill ironworks. The mill and dam were designed by John Smeaton …

Co-Curate Page
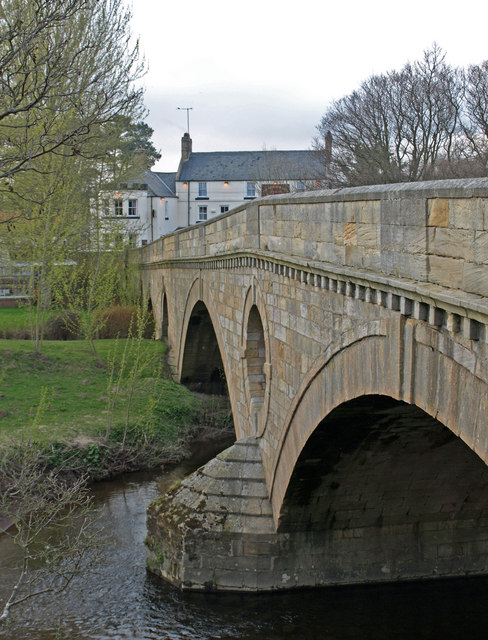
Weldon Bridge - Bridge
- Overview Map Street View The stone bridge over the River Coquet at Weldon Bridge was built c.1760[1] The bridge has 3 arches and distinctive circular openings between the arches. It …

Co-Curate Page
Rotherhope Fell Mine
- Overview Map (area 1) Map (area 2) "...The monument, which is divided into two areas, is situated on the north east side of Rotherhope Fell above Black Burn. It includes …

Co-Curate Page
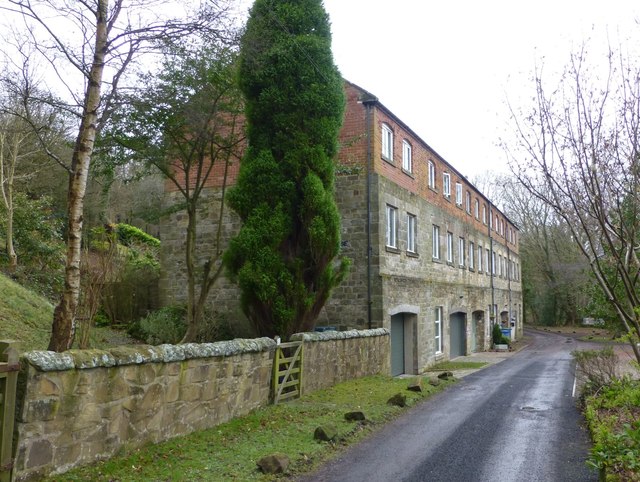
The Dye House, Acklington Park
- Overview Map Street View Dye House is a residential building on the south banks of the River Coquet in Acklington Park, about a mile south of Guyzance. It was originally …

Co-Curate Page
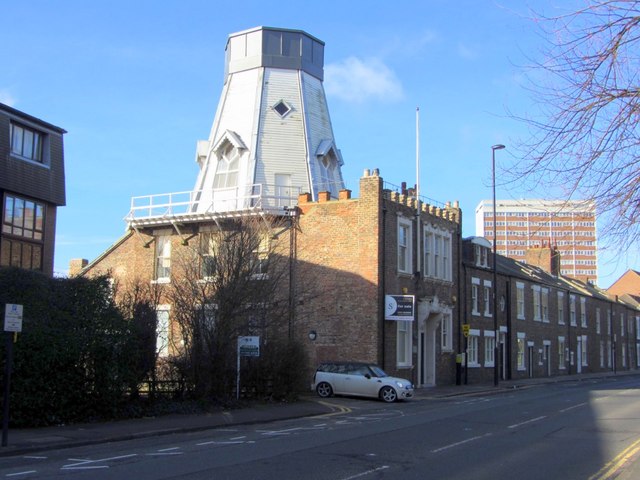
Chimney Mill
- Overview About Map Street View The Chimney Mill on Claremont Road was built in 1782 and was the first 5-sailed smock mill in Britain. The mill was powered by wind …

Co-Curate Page
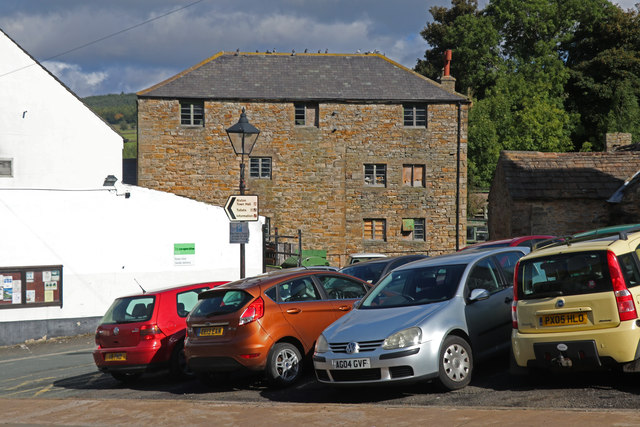
High Mill, Alston
- Overview Map Street View - Front Street View - Rear High Mill, off Front Street in Alston, was originally built as a water-powered corn mill in 1767, by the eminent …

from https://commons.wikimedia.org…
Portrait of John Smeaton
- c.1799 Public domain image c/o Wikimedia Commons. Portrait from The Royal Society.
Added by
Simon Cotterill

Co-Curate Page
Coldstream Bridge
- Overview About Coldstream Bridge Map Street View Coldstream Bridge, linking Coldstream, Scottish Borders with Cornhill-on-Tweed, Northumberland, is an 18th-century Grade II* listed bridge between England and Scotland, across the …

Co-Curate Page
Dam on the River Coquet
- Overview Map This horseshoe-shaped dam on the River Coquet was built in 1775 to provide water power for Park Mill ironworks. The mill and dam were designed by John Smeaton …

Co-Curate Page
Weldon Bridge - Bridge
- Overview Map Street View The stone bridge over the River Coquet at Weldon Bridge was built c.1760[1] The bridge has 3 arches and distinctive circular openings between the arches. It …

Co-Curate Page
Rotherhope Fell Mine
- Overview Map (area 1) Map (area 2) "...The monument, which is divided into two areas, is situated on the north east side of Rotherhope Fell above Black Burn. It includes …

Co-Curate Page
The Dye House, Acklington Park
- Overview Map Street View Dye House is a residential building on the south banks of the River Coquet in Acklington Park, about a mile south of Guyzance. It was originally …

Co-Curate Page
Chimney Mill
- Overview About Map Street View The Chimney Mill on Claremont Road was built in 1782 and was the first 5-sailed smock mill in Britain. The mill was powered by wind …