Topics > Historical Periods > 14th Century > Battle of Otterburn, 1388
Battle of Otterburn, 1388
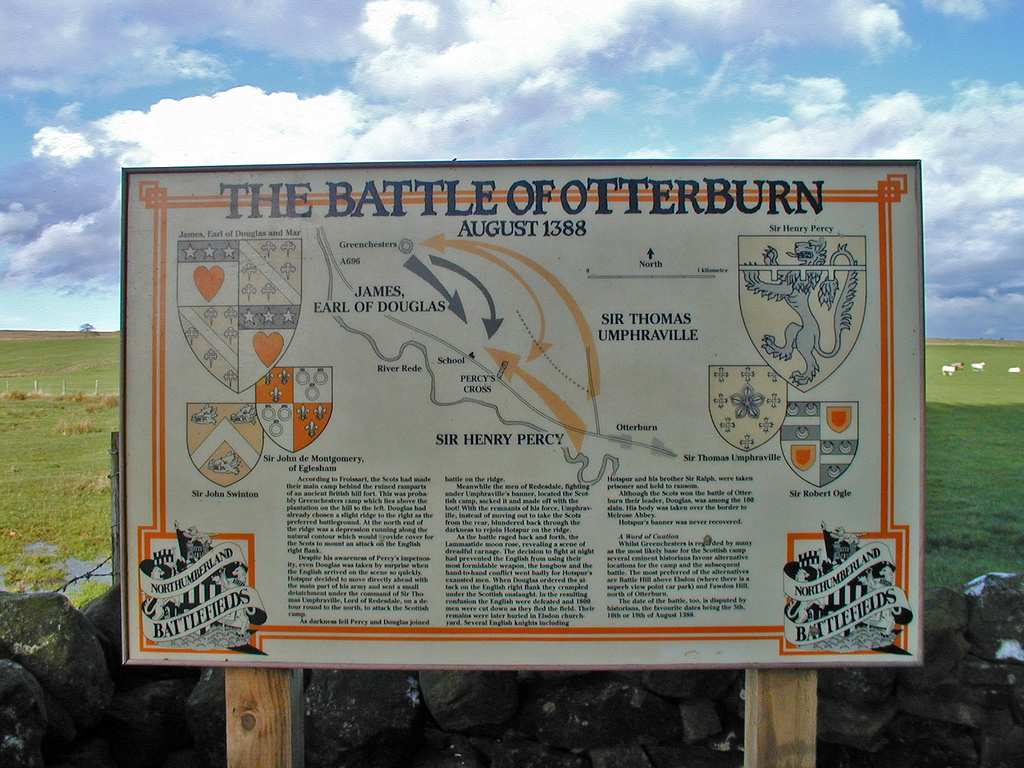
The Battle of Otterburn took place according to Scottish sources on 5 August 1388, or 19 August according to English sources, as part of the continuing border skirmishes between the Scots and English.
The best remaining record of the battle is from Jean Froissart's Chronicles in which he claims to have interviewed veterans from both sides of the battle. His account is still regarded with some concern as details, such as the distance between Newcastle upon Tyne and Otterburn, are incorrect.
The Scottish noble James, 2nd Earl of Douglas decided to lead a raid—one of a continuing series on both sides of the border—into English territory. It was timed to take advantage of divisions on the English side between Ralph Neville, 1st Earl of Westmorland and Henry Percy, 1st Earl of Northumberland who had just taken over defence of the border.
The battle
The Scots divided their forces with the main force and their baggage train heading towards Carlisle while a raiding party under the Earl of Douglas ravaged the countryside around Durham and Newcastle. Northumberland sent his two sons Harry Hotspur and Sir Ralph Percy to engage while he stayed at Alnwick to cut off the marauders' retreat.
Froissart says that the first fighting included a meeting of the Earl of Douglas and Henry Percy in hand-to-hand combat, in which Percy's pennon was captured. Douglas then moved off destroying the castle at Ponteland and besieging Otterburn Castle (now Otterburn Tower). Percy attacked Douglas's encampment with a surprise attack in the late afternoon, but first encountered the Earl's serving men, giving the bulk of the forces time to muster and attack them on their flank.
Douglas led the left wing, while John Dunbar, Earl of Moray led the right. Hotspur's men, having ridden up from Newcastle, were tired and disorganized as they made their way onto the field. Hotspur was so overly confident that he attacked the Scots while the rest of his force was still marching up through Otterburn.
During the battle on a moonlit night Douglas was killed; his death had no influence on the outcome of the battle and went unnoticed until much later. The Percys were both captured, with the remaining English force retreating to Newcastle. Despite Percy's force having an estimated three to one advantage over the Scots, Froissart records 1040 English were captured and 1860 killed whereas 200 Scots were captured and 100 were killed. The Westminster Chronicle estimates Scottish casualties at around 500. When the Bishop of Durham advanced from Newcastle with 10,000 men he was so impressed by the ordered appearance of the Scottish force, the din they set up with their horns, and their seemingly unassailable position, that he declined to attack.
Some have suggested that Hotspur's rashness and eagerness to engage the Scots and the added tiredness of the English army after its long march north, were without doubt, the reasons for English defeat, despite having a three to one advantage in numbers. It is possible that the reasons for this defeat may be more complex, however.
Aftermath
Such a decisive victory kept the two sides apart for some time. Of such renown was the battle of Otterburn that several ballads were composed in its honour including The Battle of Otterburn and The Ballad of Chevy Chase (Child ballads 161 and 162). Chevy Chase rather mangles the history of the battle and may be confusing other conflicts at around the same time but it is still cited as one of the best of the ancient ballads.
Houses involved in the battle
Some of the various Scottish Lowland families involved in this battle were the Swintons, Johnstones, Grahams, Gordons, Lindsays, Leslies, Herons and Montgomerys.
Visit the page: Battle of Otterburn for references and further details. You can contribute to this article on Wikipedia.

from Youtube (youtube)
Sir James 2nd Earl of Douglas at the Battle of Otterburn 1388
Pinned by Simon Cotterill

from http://books.google.co.uk/boo…
History of the battle of Otterburn fought in 1388. Robert White (1857)
- Book from 1857 available as a free eBook, digitised by Google.
Added by
Simon Cotterill

from http://www.battlefieldstrust.…
Battle of Otterburn - Battlefields Trust
- " The second half of the 14th century was a period of political instability both within England and Scotland and between the two countries. The truce that had existed between …
Added by
Simon Cotterill
from http://www.english-heritage.o…
Battle of Otterburn - English Heritage
- "In 1388 the Scots decided to take advantage of the disunity caused in England by the power struggle between King Richard II and the Lords Appellant by mounting a large …
Added by
Simon Cotterill

from https://commons.wikimedia.org…
Battle of Otterburn (1388).
- Miniature from Jean Froissart, Chroniques, 1399. Public domain image c/o Wikimedia Commons
Added by
Simon Cotterill
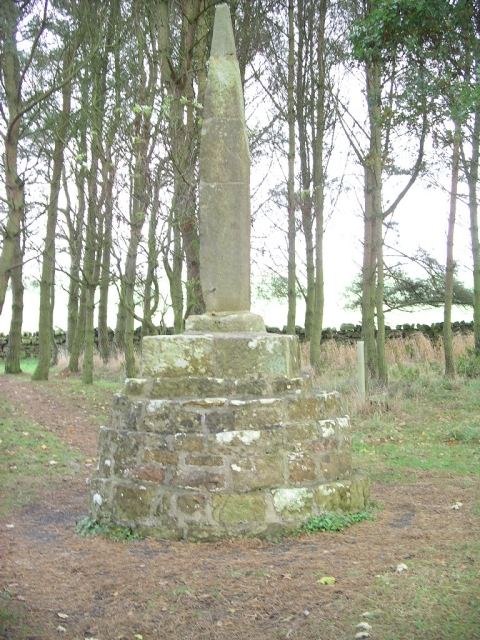

Co-Curate Page
Percy Cross
- Overview Map Percy Cross was erected to commemorate the Battle of Otterburn, 1388. It was erected on this site in 1777, incorporating the earlier medieval cross base. The shaft is …

Co-Curate Page
Outer Golden Pot
- Overview Map The Outer Golden Pot is the socket stone of a medieval wayside cross, situated in an elevated position on the western edge of Dere Street, the Roman road between …

from Youtube (youtube)
Sir James 2nd Earl of Douglas at the Battle of Otterburn 1388
Pinned by Simon Cotterill

from http://books.google.co.uk/boo…
History of the battle of Otterburn fought in 1388. Robert White (1857)
- Book from 1857 available as a free eBook, digitised by Google.
Added by
Simon Cotterill

from http://www.battlefieldstrust.…
Battle of Otterburn - Battlefields Trust
- " The second half of the 14th century was a period of political instability both within England and Scotland and between the two countries. The truce that had existed between …
Added by
Simon Cotterill

from http://www.english-heritage.o…
Battle of Otterburn - English Heritage
- "In 1388 the Scots decided to take advantage of the disunity caused in England by the power struggle between King Richard II and the Lords Appellant by mounting a large …
Added by
Simon Cotterill

from https://commons.wikimedia.org…
Battle of Otterburn (1388).
- Miniature from Jean Froissart, Chroniques, 1399. Public domain image c/o Wikimedia Commons
Added by
Simon Cotterill

Co-Curate Page
Percy Cross
- Overview Map Percy Cross was erected to commemorate the Battle of Otterburn, 1388. It was erected on this site in 1777, incorporating the earlier medieval cross base. The shaft is …