Evaluating the effectiveness of restoring longitudinal connectivity for stream fish communities: towards a more holistic approach

-
Description
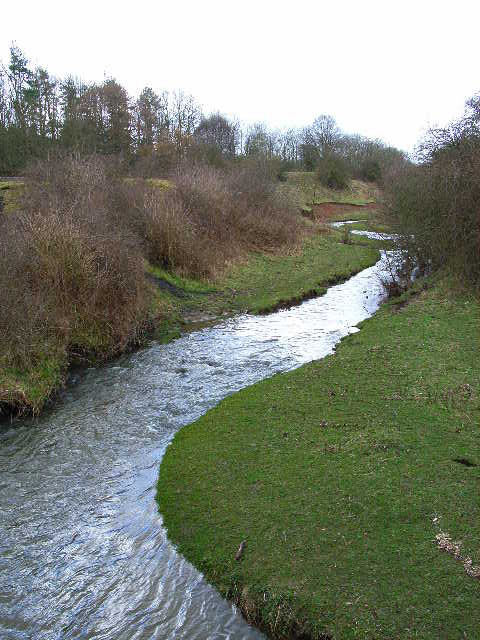
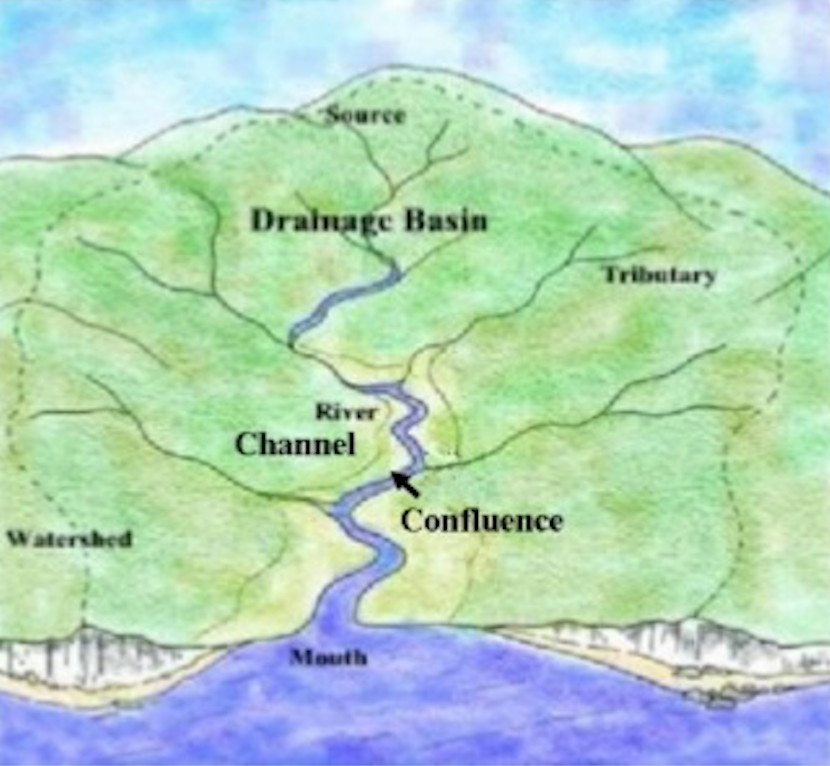
Journal article: Tummers, Jeroen S., Hudson, Steve, Lucas, Martyn C. Evaluating the effectiveness of restoring longitudinal connectivity for stream fish communities: towards a more holistic approach. Science of The Total Environment. 2016 vol 569-570, pp 850-860. ABSTRACT A more holistic approach towards testing longitudinal connectivity restoration is needed in order to establish that intended ecological functions of such restoration are achieved. We illustrate the use of a multi-method scheme to evaluate the effectiveness of ‘nature-like’ connectivity restoration for stream fish communities in the River Deerness, NE England. Electric-fishing, capture-mark-recapture, PIT telemetry and radio-telemetry were used to measure fish community composition, dispersal, fishway efficiency and upstream migration respectively. For measuring passage and dispersal, our rationale was to evaluate a wide size range of strong swimmers (exemplified by brown trout Salmo trutta) and weak swimmers (exemplified by bullhead Cottus perifretum) in situ in the stream ecosystem. Radio-tracking of adult trout during the spawning migration showed that passage efficiency at each of five connectivity-restored sites was 81.3–100%. Unaltered (experimental control) structures on the migration route had a bottle-neck effect on upstream migration, especially during low flows. However, even during low flows, displaced PIT tagged juvenile trout (total n = 153) exhibited a passage efficiency of 70.1–93.1% at two nature-like passes. In mark-recapture experiments juvenile brown trout and bullhead tagged (total n = 5303) succeeded in dispersing upstream more often at most structures following obstacle modification, but not at the two control sites, based on a Laplace kernel modelling approach of observed dispersal distance and barrier traverses. Medium-term post-restoration data (2–3 years) showed that the fish assemblage remained similar at five of six connectivity-restored sites and two control sites, but at one connectivity-restored headwater site previously inhabited by trout only, three native non-salmonid species colonized. We conclude that stream habitat reconnection should support free movement of a wide range of species and life stages, wherever retention of such obstacles is not needed to manage non-native invasive species. Evaluation of the effectiveness of fish community restoration in degraded streams benefits from a similarly holistic approach. -
Owner
Science of The Total Environment -
Source
Local (Co-Curate) -
License
What does this mean? Unknown license check permission to reuse
-
Further information
Link: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.06.207
Resource type: Text/Website
Added by: Simon Cotterill
Last modified: 7 years, 11 months ago
Viewed: 814 times
Picture Taken: Unknown -
Co-Curate tags