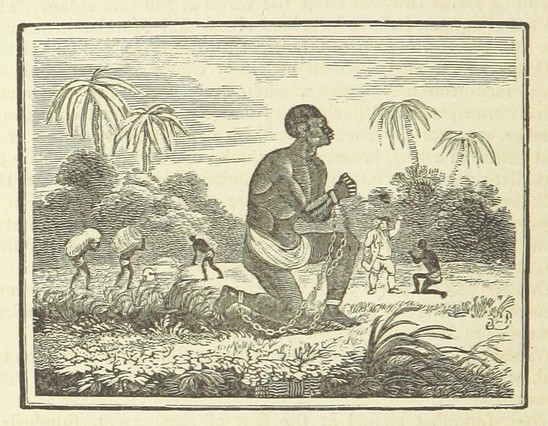
Coloured lithograph of slaves picking cotton. Fort Sumter Museum Charleston .

-
Description
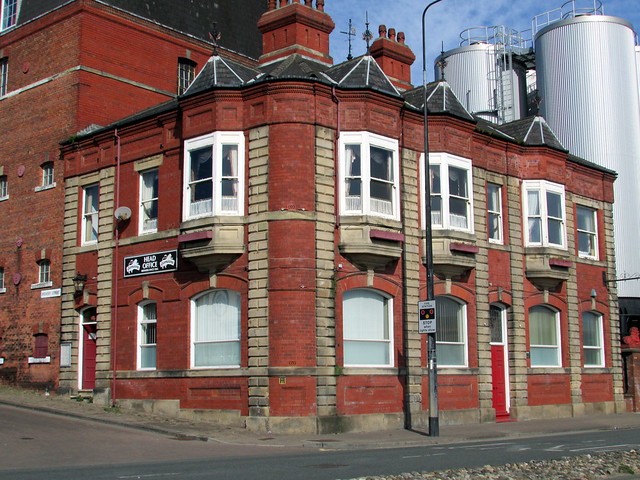
Charleston in the Antebellum Era. Also in the central square is a statue of Senator John Calhoun high on a stone column. It is said the statue is so high to prevent the former slaves from defacing it! But who could blame them as Calhoun was a rabid racist. He was one of many racist slave owners who dominated the Sth Carolina legislature. It enacted new slave codes in 1800 and 1820 to make manumission (freeing so slaves) almost impossible. Calhoun in Washington was the one who led the crisis about secession in 1832. Sth Carolina threaded to secede from the Union over a tariff bill. Sth Carolina and its politicians were always champions of slavery and states’ rights. Then in 1822 Denmark Vesey, a slave who had purchased his freedom before the new laws of 1820, planned a major bloodbath in Charleston. Thousands of slaves in Charleston knew about the planned uprising but eventually two ratted on Vesey and he was arrested before the uprising began. 131 slaves were charged with conspiracy and 35 hung, including Vesey. His little house in Charleston (probably not the actual one) is now a National Landmark. It was also a Sth Carolinian Congressman in 1835 who got the “gag rule” passed in Congress to stop Abolitionist pamphlets and mail going to the South. It passed in 1836 and was known as the Pinckney Resolution. It was finally rescinded in 1844 when the Northern Democrats got control of Congress. Later in 1856 it was Congressman Preston Brooks of Sth Carolina who led the attack on the pro-slavery Northerner Charles Sumner on the floor of the US Senate. Sumner (a Republican like Lincoln) was bashed with a cane whilst pro-slavery Southern friends of Brooks protected him from irate Northern Senators who could do nothing to help Charles Sumner. Sumner took over three years to recover from this attack. This was one of the finale events that polarised anti-Southern and pro-slavery abolition support in the North. Sth Carolina always led the vanguard of propaganda against the Abolitionists and against the North. But they also had much to fear. In coastal Sth Carolina slaves outnumbered whites and when the white planters retreated to Charleston for the summer season, many rural counties became 98% black slave. In the 1850s Sth Carolinians became more and more militant and not surprisingly they were the first state to vote for secession upon the election of Abraham Lincoln in 1860. They wanted to protect their privileged and gracious life style of which we can see remnants today in Charleston –the beautiful mansions and public buildings. In this antebellum period Charleston was extremely wealthy as the major importing and exporting port of the South. It handled the cotton from upstate and a large part of the slave market. The international slave trade was banned from 1808 but many shiploads of black slaves still entered American illegally after that date. The wealthy planting class imported their chandeliers from France, their fine furniture and porcelain from England and their silk fabrics for the ladies ball gowns from Paris. In your free afternoon you can enter some of these mansions and see theirs and their slaves’ living conditions especially at the Aiken-Rhett house. Charleston during the Civil War. The first shots of the Civil War were fired in Charleston Harbour by the Confederates but few shots were fired at Charleston by the Union forces. A small battle outside the city in 1862 saw the Confederates being victorious and the Unions forces retreating. That ended any immediate threat of land invasion of Charleston. Charleston Harbour had always been well protected with forts in addition to Fort Sumter in case of Spanish or British attack. The Confederates used these forts to protect the city. But the Anaconda Plan meant that from the start of the Civil War the Union naval blockade was reasonably successful. Gun runners still managed to bring supplies into Charleston from France but goods were limited. In the latter stages of the Civil War, Charleston like other areas of the South was basically without food for whites or slaves. People were starving. Yet despite this in the final year of the Civil War the Charlestonians still had their grand balls for the season with French ball gowns smuggled into the city when some were starving. At the same time General Vance with his North Carolina Army was enduring the freezing winter of northern Virginia with his troops in thread bare uniforms and worn boots. But resources from Sth Carolina were not advanced to help the troops from North Carolina. They were kept aside for Sth Carolina. This was one of the many great weaknesses of the Confederacy- blind obsession with states’ rights. The continuing extravagances of the Charlestonian elite also angered starving Southerners and added to the decline in morale in the South. In February 1865 when General Sherman advanced towards Charleston from Savannah the Confederate General Beauregard, ordered the evacuation of Confederate troops from Charleston. The Mayor of Charleston was then able to surrender to Sherman and avoid the city being bombarded or destroyed. We must be thankful for that and the decision of the ladies of Charleston to preserve as many historic houses as they could. They began this around 1955. -
Owner
denisbin -
Source
Flickr (Flickr) -
License
What does this mean? Attribution-NoDerivs License
-
Further information
Link: https://www.flickr.com/photos/82134796@N03/13683296255/
Resource type: Image
Added by: Simon Cotterill
Last modified: 5 years, 7 months ago
Viewed: 1009 times
Picture Taken: 2013-05-21T11:27:42 -
Co-Curate tags